CTCF-binding element regulates ESC differentiation via orchestrating long-range chromatin interaction between enhancers and HoxA
- PMID: 33581110
- PMCID: PMC7960549
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100413
CTCF-binding element regulates ESC differentiation via orchestrating long-range chromatin interaction between enhancers and HoxA
Erratum in
-
Correction: CTCF-binding element regulates ESC differentiation via orchestrating long-range chromatin interaction between enhancers and HoxA.J Biol Chem. 2022 Nov;298(11):102653. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102653. Epub 2022 Nov 5. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 36347102 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
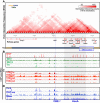
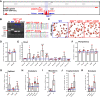
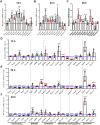
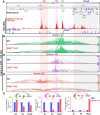
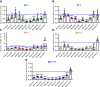
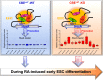
Proper expression of Homeobox A cluster genes (HoxA) is essential for embryonic stem cell (ESC) differentiation and individual development. However, mechanisms controlling precise spatiotemporal expression of HoxA during early ESC differentiation remain poorly understood. Herein, we identified a functional CTCF-binding element (CBE+47) closest to the 3'-end of HoxA within the same topologically associated domain (TAD) in ESC. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated deletion of CBE+47 significantly upregulated HoxA expression and enhanced early ESC differentiation induced by retinoic acid (RA) relative to wild-type cells. Mechanistic analysis by chromosome conformation capture assay (Capture-C) revealed that CBE+47 deletion decreased interactions between adjacent enhancers, enabling formation of a relatively loose enhancer-enhancer interaction complex (EEIC), which overall increased interactions between that EEIC and central regions of HoxA chromatin. These findings indicate that CBE+47 organizes chromatin interactions between its adjacent enhancers and HoxA. Furthermore, deletion of those adjacent enhancers synergistically inhibited HoxA activation, suggesting that these enhancers serve as an EEIC required for RA-induced HoxA activation. Collectively, these results provide new insight into RA-induced HoxA expression during early ESC differentiation, also highlight precise regulatory roles of the CTCF-binding element in orchestrating high-order chromatin structure.
Keywords: CTCF-binding element; HoxA; differentiation; embryonic stem cells; enhancer; enhancer–enhancer interaction complex; long-range chromatin interaction.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enhancer architecture-dependent multilayered transcriptional regulation orchestrates RA signaling-induced early lineage differentiation of ESCs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Nov 18;49(20):11575-11595. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1001. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34723340 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation-independent removable insulator controls chromatin remodeling at the HOXA locus via retinoic acid signaling.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Dec 15;25(24):5383-5394. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw354. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 27798106
-
Opposing Roles for the lncRNA Haunt and Its Genomic Locus in Regulating HOXA Gene Activation during Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation.Cell Stem Cell. 2015 May 7;16(5):504-16. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2015.03.007. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Cell Stem Cell. 2015. PMID: 25891907
-
The structural and functional roles of CTCF in the regulation of cell type-specific and human disease-associated super-enhancers.Genes Genomics. 2019 Mar;41(3):257-265. doi: 10.1007/s13258-018-0768-z. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Genes Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30456521 Review.
-
CTCF shapes chromatin structure and gene expression in health and disease.EMBO Rep. 2022 Sep 5;23(9):e55146. doi: 10.15252/embr.202255146. Epub 2022 Aug 22. EMBO Rep. 2022. PMID: 35993175 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sequential in cis mutagenesis in vivo reveals various functions for CTCF sites at the mouse HoxD cluster.Genes Dev. 2021 Nov 1;35(21-22):1490-1509. doi: 10.1101/gad.348934.121. Epub 2021 Oct 28. Genes Dev. 2021. PMID: 34711654 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenome rewiring in human pluripotent stem cells.Trends Cell Biol. 2022 Mar;32(3):259-271. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2021.12.001. Epub 2021 Dec 23. Trends Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 34955367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic regulatory reconstitution reveals principles of mammalian Hox cluster regulation.Science. 2022 Jul;377(6601):eabk2820. doi: 10.1126/science.abk2820. Epub 2022 Jul 1. Science. 2022. PMID: 35771912 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancer architecture-dependent multilayered transcriptional regulation orchestrates RA signaling-induced early lineage differentiation of ESCs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Nov 18;49(20):11575-11595. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1001. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34723340 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic regulation of CTCF expression and chromatin association dictates starvation response in mice and flies.iScience. 2023 Jun 15;26(7):107128. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107128. eCollection 2023 Jul 21. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37416476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takahashi K., Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663–676. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K., Tanabe K., Ohnuki M., Narita M., Ichisaka T., Tomoda K., Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007;131:861–872. - PubMed
-
- Sato N., Meijer L., Skaltsounis L., Greengard P., Brivanlou A.H. Maintenance of pluripotency in human and mouse embryonic stem cells through activation of Wnt signaling by a pharmacological GSK-3-specific inhibitor. Nat. Med. 2004;10:55–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

