Trio family proteins as regulators of cell migration and morphogenesis in development and disease - mechanisms and cellular contexts
- PMID: 33568469
- PMCID: PMC7888718
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.248393
Trio family proteins as regulators of cell migration and morphogenesis in development and disease - mechanisms and cellular contexts
Erratum in
-
Correction: Trio family proteins as regulators of cell migration and morphogenesis in development and disease - mechanisms and cellular contexts.J Cell Sci. 2023 Feb 1;136(3):jcs260984. doi: 10.1242/jcs.260984. Epub 2023 Feb 10. J Cell Sci. 2023. PMID: 36763488 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
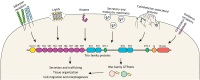
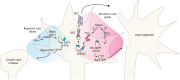
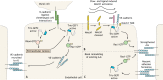
The well-studied members of the Trio family of proteins are Trio and kalirin in vertebrates, UNC-73 in Caenorhabditis elegans and Trio in Drosophila Trio proteins are key regulators of cell morphogenesis and migration, tissue organization, and secretion and protein trafficking in many biological contexts. Recent discoveries have linked Trio and kalirin to human disease, including neurological disorders and cancer. The genes for Trio family proteins encode a series of large multidomain proteins with up to three catalytic activities and multiple scaffolding and protein-protein interaction domains. As such, Trio family proteins engage a wide array of cell surface receptors, substrates and interaction partners to coordinate changes in cytoskeletal regulatory and protein trafficking pathways. We provide a comprehensive review of the specific mechanisms by which Trio family proteins carry out their functions in cells, highlight the biological and cellular contexts in which they occur, and relate how alterations in these functions contribute to human disease.
Keywords: Cell morphogenesis; Cytoskeleton; Neurodevelopmental disorders; Rho GTPase; Signal transduction; Trio family.
© 2021. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Distinct cell guidance pathways controlled by the Rac and Rho GEF domains of UNC-73/TRIO in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2012 Jan;190(1):129-42. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.134429. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 21996675 Free PMC article.
-
Phagocytosis of apoptotic cells is regulated by a UNC-73/TRIO-MIG-2/RhoG signaling module and armadillo repeats of CED-12/ELMO.Curr Biol. 2004 Dec 29;14(24):2208-16. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.12.029. Curr Biol. 2004. PMID: 15620647
-
UNC-40/DCC, SAX-3/Robo, and VAB-1/Eph polarize F-actin during embryonic morphogenesis by regulating the WAVE/SCAR actin nucleation complex.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(8):e1002863. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002863. Epub 2012 Aug 2. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22876199 Free PMC article.
-
Function and regulation of the Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor Trio.Small GTPases. 2014;5:e29769. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.29769. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 24987837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic analysis of growth cone migrations in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Neurobiol. 2000 Aug;44(2):281-8. J Neurobiol. 2000. PMID: 10934329 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenic TRIO variants associated with neurodevelopmental disorders perturb the molecular regulation of TRIO and axon pathfinding in vivo.Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Apr;28(4):1527-1544. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-01963-x. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Mol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36717740
-
Functional Classification and Interaction Selectivity Landscape of the Human SH3 Domain Superfamily.Cells. 2024 Jan 20;13(2):195. doi: 10.3390/cells13020195. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38275820 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of tumour immune microenvironment-related alternative splicing events for the prognostication of pancreatic adenocarcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2021 Nov 12;21(1):1211. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08962-7. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34772375 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro fluorescence assay to measure GDP/GTP exchange of guanine nucleotide exchange factors of Rho family GTPases.Biol Methods Protoc. 2021 Dec 31;7(1):bpab024. doi: 10.1093/biomethods/bpab024. eCollection 2022. Biol Methods Protoc. 2021. PMID: 35087952 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA-binding protein Nab2 regulates levels of the RhoGEF Trio to govern axon and dendrite morphology.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Aug 1;35(8):ar109. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E24-04-0150. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38985523 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamowicz, M., Radlwimmer, B., Rieker, R. J., Mertens, D., Schwarzbach, M., Schraml, P., Benner, A., Lichter, P., Mechtersheimer, G. and Joos, S. (2006). Frequent amplifications and abundant expression of Trio, NKD2, and IRX2 in soft tissue sarcomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 45, 829-838. 10.1002/gcc.20343 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alam, M. R., Johnson, R. C., Darlington, D. N., Hand, T. A., Mains, R. E. and Eipper, B. A. (1997). Kalirin, a cytosolic protein with spectrin-like and GDP/GTP exchange factor-like domains that interacts with peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase, an integral membrane peptide-processing enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 12667-12675. 10.1074/jbc.272.19.12667 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alexander, M., Selman, G., Seetharaman, A., Chan, K. K. M., D'Souza, S. A., Byrne, A. B. and Roy, P. J. (2010). MADD-2, a homolog of the Opitz syndrome protein MID1, regulates guidance to the midline through UNC-40 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Cell 18, 961-972. 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.05.016 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

