Functional P2X7 Receptors in the Auditory Nerve of Hearing Rodents Localize Exclusively to Peripheral Glia
- PMID: 33563723
- PMCID: PMC8018736
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2240-20.2021
Functional P2X7 Receptors in the Auditory Nerve of Hearing Rodents Localize Exclusively to Peripheral Glia
Abstract
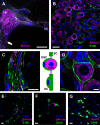
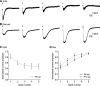
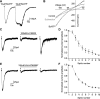
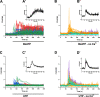
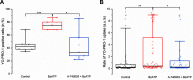
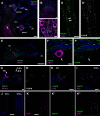
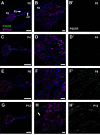
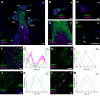
P2X7 receptors (P2X7Rs) are associated with numerous pathophysiological mechanisms, and this promotes them as therapeutic targets for certain neurodegenerative conditions. However, the identity of P2X7R-expressing cells in the nervous system remains contentious. Here, we examined P2X7R functionality in auditory nerve cells from rodents of either sex, and determined their functional and anatomic expression pattern. In whole-cell recordings from rat spiral ganglion cultures, the purinergic agonist 2',3'-O-(4-benzoylbenzoyl)-ATP (BzATP) activated desensitizing currents in spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs) but non-desensitizing currents in glia that were blocked by P2X7R-specific antagonists. In imaging experiments, BzATP gated sustained Ca2+ entry into glial cells. BzATP-gated uptake of the fluorescent dye YO-PRO-1 was reduced and slowed by P2X7R-specific antagonists. In rats, P2X7Rs were immuno-localized predominantly within satellite glial cells (SGCs) and Schwann cells (SCs). P2X7R expression was not detected in the portion of the auditory nerve within the central nervous system. Mouse models allowed further exploration of the distribution of cochlear P2X7Rs. In GENSAT reporter mice, EGFP expression driven via the P2rx7 promoter was evident in SGCs and SCs but was undetectable in SGNs. A second transgenic model showed a comparable cellular distribution of EGFP-tagged P2X7Rs. In wild-type mice the discrete glial expression was confirmed using a P2X7-specific nanobody construct. Our study shows that P2X7Rs are expressed by peripheral glial cells, rather than by afferent neurons. Description of functional signatures and cellular distributions of these enigmatic proteins in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) will help our understanding of ATP-dependent effects contributing to hearing loss and other sensory neuropathies.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT P2X7 receptors (P2X7Rs) have been the subject of much scrutiny in recent years. They have been promoted as therapeutic targets in a number of diseases of the nervous system, yet the specific cellular location of these receptors remains the subject of intense debate. In the auditory nerve, connecting the inner ear to the brainstem, we show these multimodal ATP-gated channels localize exclusively to peripheral glial cells rather than the sensory neurons, and are not evident in central glia. Physiologic responses in the peripheral glia display classical hallmarks of P2X7R activation, including the formation of ion-permeable and also macromolecule-permeable pores. These qualities suggest these proteins could contribute to glial-mediated inflammatory processes in the auditory periphery under pathologic disease states.
Keywords: ATP; P2X; cochlea; deafness; hearing; purinergic.
Copyright © 2021 the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
P2X7 receptors in satellite glial cells mediate high functional expression of P2X3 receptors in immature dorsal root ganglion neurons.Mol Pain. 2012 Feb 7;8:9. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-8-9. Mol Pain. 2012. PMID: 22314033 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent membrane properties of mouse cochlear glial cells around hearing onset.J Neurosci Res. 2021 Feb;99(2):679-698. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24744. Epub 2020 Oct 25. J Neurosci Res. 2021. PMID: 33099767
-
Activation of P2X7 receptors in glial satellite cells reduces pain through downregulation of P2X3 receptors in nociceptive neurons.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Oct 28;105(43):16773-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801793105. Epub 2008 Oct 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18946042 Free PMC article.
-
P2X7 receptors: channels, pores and more.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2012 Sep;11(6):705-21. doi: 10.2174/187152712803581137. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 22963440 Review.
-
P2X7 Receptors Amplify CNS Damage in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 20;21(17):5996. doi: 10.3390/ijms21175996. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32825423 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Animal Models for the Investigation of P2X7 Receptors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 4;24(9):8225. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098225. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purinergic Signalling in the Cochlea.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 28;23(23):14874. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314874. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age-related changes in P2Y receptor signalling in mouse cochlear supporting cells.J Physiol. 2023 Oct;601(19):4375-4395. doi: 10.1113/JP284980. Epub 2023 Sep 16. J Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37715703 Free PMC article.
-
P2X7 receptor antagonists modulate experimental autoimmune neuritis via regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and Th17 and Th1 cell differentiation.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Mar 25;21(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03057-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38528529 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhattacharya A, Wang Q, Ao H, Shoblock JR, Lord B, Aluisio L, Fraser I, Nepomuceno D, Neff RA, Welty N, Lovenberg TW, Bonaventure P, Wickenden AD, Letavic MA (2013) Pharmacological characterization of a novel centrally permeable P2X7 receptor antagonist: JNJ-47965567. Br J Pharmacol 170:624–640. 10.1111/bph.12314 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
