Cutting Edge of the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis: Sphingomyelin Deacylase, the Enzyme Involved in Its Ceramide Deficiency, Plays a Pivotal Role
- PMID: 33562655
- PMCID: PMC7916095
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22041613
Cutting Edge of the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis: Sphingomyelin Deacylase, the Enzyme Involved in Its Ceramide Deficiency, Plays a Pivotal Role
Abstract
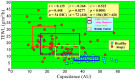
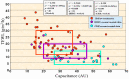
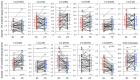
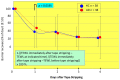
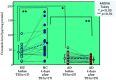
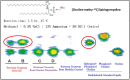
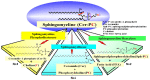
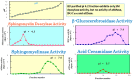
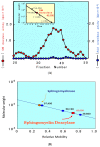
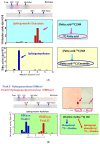
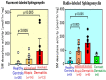
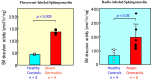
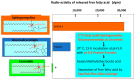
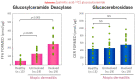
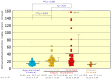
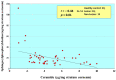
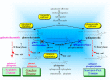
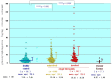
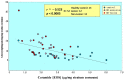
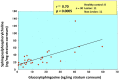
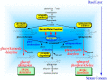
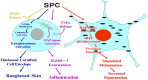
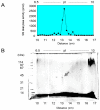
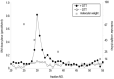
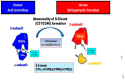
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is characterized clinically by severe dry skin and functionally by both a cutaneous barrier disruption and an impaired water-holding capacity in the stratum corneum (SC) even in the nonlesional skin. The combination of the disrupted barrier and water-holding functions in nonlesional skin is closely linked to the disease severity of AD, which suggests that the barrier abnormality as well as the water deficiency are elicited as a result of the induced dermatitis and subsequently trigger the recurrence of dermatitis. These functional abnormalities of the SC are mainly attributable to significantly decreased levels of total ceramides and the altered ceramide profile in the SC. Clinical studies using a synthetic pseudo-ceramide (pCer) that can function as a natural ceramide have indicated the superior clinical efficacy of pCer and, more importantly, have shown that the ceramide deficiency rather than changes in the ceramide profile in the SC of AD patients plays a central role in the pathogenesis of AD. Clinical studies of infants with AD have shown that the barrier disruption due to the ceramide deficiency is not inherent and is essentially dependent on postinflammatory events in those infants. Consistently, the recovery of trans-epidermal water loss after tape-stripping occurs at a significantly slower rate only at 1 day post-tape-stripping in AD skin compared with healthy control (HC) skin. This resembles the recovery pattern observed in Niemann-Pick disease, which is caused by an acid sphingomyelinase (aSMase) deficiency. Further, comparison of ceramide levels in the SC between before and after tape-stripping revealed that whereas ceramide levels in HC skin are significantly upregulated at 4 days post-tape-stripping, their ceramide levels remain substantially unchanged at 4 days post-tape-stripping. Taken together, the sum of these findings strongly suggests that an impaired homeostasis of a ceramide-generating process may be associated with these abnormalities. We have discovered a novel enzyme, sphingomyelin (SM) deacylase, which cleaves the N-acyl linkage of SM and glucosylceramide (GCer). The activity of SM deacylase is significantly increased in AD lesional epidermis as well as in the involved and uninvolved SC of AD skin, but not in the skin of patients with contact dermatitis or chronic eczema, compared with HC skin. SM deacylase competes with aSMase and β-glucocerebrosidase (BGCase) to hydrolyze their common substrates, SM and GCer, to yield their lysoforms sphingosylphosphorylcholine (SPC) and glucosylsphingosine (GSP), respectively, instead of ceramide. Consistently, those reaction products (SPC and GSP) accumulate to a greater extent in the involved and uninvolved SC of AD skin compared with chronic eczema or contact dermatitis skin as well as HC skin. Successive chromatographies were used to purify SM deacylase to homogeneity with a single band of ≈43 kDa and with an enrichment of >14,000-fold. Analysis of a protein spot with SM deacylase activity separated by 2D-SDS-PAGE using MALDI-TOF MS/MS allowed its amino acid sequence to be determined and to identify it as the β-subunit of acid ceramidase (aCDase), an enzyme consisting of α- and β-subunits linked by amino-bonds and a single S-S bond. Western blotting of samples treated with 2-mercaptoethanol revealed that whereas recombinant human aCDase was recognized by antibodies to the α-subunit at ≈56 and ≈13 kDa and the β-subunit at ≈43 kDa, the purified SM deacylase was detectable only by the antibody to the β-subunit at ≈43 kDa. Breaking the S-S bond of recombinant human aCDase with dithiothreitol elicited the activity of SM deacylase with an apparent size of ≈40 kDa upon gel chromatography in contrast to aCDase activity with an apparent size of ≈50 kDa in untreated recombinant human aCDase. These results provide new insights into the essential role of SM deacylase as the β-subunit aCDase that causes the ceramide deficiency in AD skin.
Keywords: atopic dermatitis; barrier function; ceramides; pathogenesis; sphingomyelin deacylase.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Sphingomyelin Deacylase, the Enzyme Involved in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis, Is Identical to the β-Subunit of Acid Ceramidase.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 20;21(22):8789. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228789. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33233706 Free PMC article.
-
A possible mechanism underlying the ceramide deficiency in atopic dermatitis: expression of a deacylase enzyme that cleaves the N-acyl linkage of sphingomyelin and glucosylceramide.J Dermatol Sci. 2009 Jul;55(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2009.04.006. Epub 2009 May 13. J Dermatol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19443184 Review.
-
High-expression of sphingomyelin deacylase is an important determinant of ceramide deficiency leading to barrier disruption in atopic dermatitis.J Invest Dermatol. 2000 Sep;115(3):406-13. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2000.00072.x. J Invest Dermatol. 2000. PMID: 10951276
-
The skin of atopic dermatitis patients contains a novel enzyme, glucosylceramide sphingomyelin deacylase, which cleaves the N-acyl linkage of sphingomyelin and glucosylceramide.Biochem J. 2000 Sep 15;350 Pt 3(Pt 3):747-56. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 10970788 Free PMC article.
-
Role of ceramides in barrier function of healthy and diseased skin.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2005;6(4):215-23. doi: 10.2165/00128071-200506040-00002. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2005. PMID: 16060709 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of Lipids in the Permeability Barriers of Skin and Oral Mucosa.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 15;22(10):5229. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105229. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34063352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucosylsphingosine evokes pruritus via activation of 5-HT2A receptor and TRPV4 in sensory neurons.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 May;179(10):2193-2207. doi: 10.1111/bph.15733. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34766332 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Omega-Hydroxy Ceramides in Epidermis: Biosynthesis, Barrier Integrity and Analyzing Method.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 6;24(5):5035. doi: 10.3390/ijms24055035. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Children with atopic dermatitis show increased activity of β-glucocerebrosidase and stratum corneum levels of glucosylcholesterol that are strongly related to the local cytokine milieu.Br J Dermatol. 2022 Jun;186(6):988-996. doi: 10.1111/bjd.20979. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Br J Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 34993951 Free PMC article.
-
A review of the efficacy of popular eye cream ingredients.Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024 Jun 13;10(2):e156. doi: 10.1097/JW9.0000000000000156. eCollection 2024 Jun. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38873621 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nettis E., Ortoncelli M., Pellacani G., Foti C., Leo E.D., Patruno C., Rongioletti F., Argenziano G., Ferrucci S.M., Macchia L., et al. A multicenter study on the prevalence of clinical patterns and clinical phenotypes in adult atopic dermatitis. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2020;30:448–450. doi: 10.18176/jiaci.0519. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Imokawa G., Ishida K. Role of ceramide in the barrier function of the stratum corneum, Implications for the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. J. Clin. Exp. Derm. Res. 2014;5:206–218. doi: 10.4172/2155-9554.1000206. - DOI
-
- Hata M., Tokura Y., Takigawa M., Sato M., Shioya Y., Fujikura Y., Imokawa G. Assessment of epidermal barrier function by photoacoustic spectrometry in relation to its importance in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Lab. Investig. 2002;82:1451–1461. doi: 10.1097/01.LAB.0000036874.83540.2B. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Matsuki H., Kiyokane K., Matsuki T., Sato S., Imokawa G. Re-characterization of the non-lesional dry skin in atopic dermatitits through disrupted barrier function. Exog. Derm. 2004;3:282–292. doi: 10.1159/000091909. - DOI
-
- Hata M., Tokura Y., Takigawa M., Tamura Y., Imokawa G. Efficacy of using pseudoCeramide-containg cream for the treatment of atopic dry skin in comparison with urea cream. Nishihihon J. Derm. 2002;64:606–611. doi: 10.2336/nishinihonhifu.64.606. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

