Isolation and Characterization of Feline Wharton's Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- PMID: 33562192
- PMCID: PMC7915203
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci8020024
Isolation and Characterization of Feline Wharton's Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Abstract
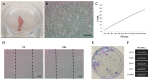
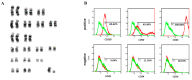
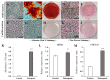
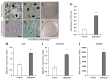
Wharton's jelly is a well-known mesenchymal stem cell source in many species, including humans. However, there have been no reports confirming the presence of mesenchymal stem cells in Wharton's jelly in cats. The purpose of this study was to isolate mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) from the Wharton's jelly of cats and to characterize stem cells. In this study, feline Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells (fWJ-MSCs) were isolated and successfully cultured. fWJ-MSCs were maintained and the proliferative potential was measured by cumulative population doubling level (CPDL) test, scratch test, and colony forming unit (CFU) test. Stem cell marker, karyotyping and immunophenotyping analysis by flow cytometry showed that fWJ-MSCs possessed characteristic mesenchymal stem cell markers. To confirm the differentiation potential, we performed osteogenic, adipogenic and chondrogenic induction under each differentiation condition. fWJ-MSCs has the ability to differentiate into multiple lineages, including osteogenic, adipogenic and chondrogenic differentiation. This study shows that Wharton's jelly of cat can be a good source of mesenchymal stem cells. In addition, fWJ-MSCs may be useful for stem cell-based therapeutic applications in feline medicine.
Keywords: Wharton’s jelly; characterization; feline; mesenchymal stem cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of the article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isolation and characterization of canine Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Cell Transplant. 2012;21(7):1493-502. doi: 10.3727/096368912X647207. Cell Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22732242
-
Human umbilical cord Wharton's Jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into nerve-like cells.Chin Med J (Engl). 2005 Dec 5;118(23):1987-93. Chin Med J (Engl). 2005. PMID: 16336835
-
Wharton's Jelly Derived-Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Isolation and Characterization.Acta Med Iran. 2018 Jan;56(1):28-33. Acta Med Iran. 2018. PMID: 29436792
-
Human Wharton's Jelly-Cellular Specificity, Stemness Potency, Animal Models, and Current Application in Human Clinical Trials.J Clin Med. 2020 Apr 12;9(4):1102. doi: 10.3390/jcm9041102. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32290584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wharton's jelly derived mesenchymal stromal cells: Biological properties, induction of neuronal phenotype and current applications in neurodegeneration research.Acta Histochem. 2015 May-Jun;117(4-5):329-38. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Acta Histochem. 2015. PMID: 25747736 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation and characterization of feline dental pulp stem cells.J Feline Med Surg. 2023 Feb;25(2):1098612X221150625. doi: 10.1177/1098612X221150625. J Feline Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 36745130 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes Derived from Feline Adipose Tissue Enhance the Effects of Anti-Inflammation Compared to Fibroblasts-Derived Exosomes.Vet Sci. 2021 Sep 3;8(9):182. doi: 10.3390/vetsci8090182. Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34564576 Free PMC article.
-
Feline umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: isolation, identification, and antioxidative stress role through NF-κB signaling pathway.Front Vet Sci. 2023 May 25;10:1203012. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1203012. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37303730 Free PMC article.
-
Altered properties of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cell during continuous in vitro cultivation.Cytotechnology. 2021 Aug;73(4):657-667. doi: 10.1007/s10616-021-00486-z. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Cytotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34349354 Free PMC article.
-
Survival and Neurogenesis-Promoting Effects of the Co-Overexpression of BCLXL and BDNF Genes on Wharton's Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Life (Basel). 2022 Sep 9;12(9):1406. doi: 10.3390/life12091406. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36143442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- La Rocca G., Anzalone R., Corrao S., Magno F., Loria T., Lo Iacono M., Di Stefano A., Giannuzzi P., Marasà L., Cappello F., et al. Isolation and characterization of Oct-4+/HLA-G+ mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord matrix: Differentiation potential and detection of new markers. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2009;131:267–282. doi: 10.1007/s00418-008-0519-3. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

