Investigation of the synergistic effect of glimepiride and rosuvastatin on alloxan-induced diabetic rat
- PMID: 33553033
- PMCID: PMC7843842
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-020-00662-6
Investigation of the synergistic effect of glimepiride and rosuvastatin on alloxan-induced diabetic rat
Abstract
Purpose: Diabetes mellitus is characterized by having a multitude of life-threatening secondary complications, particularly dyslipidemia, which ultimately leads to the development of comorbid diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases. This research work was designed to investigate the synergistic effect of glimepiride (1 mg/kg b.w.) and rosuvastatin (10 mg /kg b.w.) on alloxan-induced diabetic rats having dyslipidemia.
Methods: Diabetes was induced by injecting alloxan (120 mg/kg b.w.) intraperitoneally. The experiment was conducted to determine the level of blood glucose, HbA1c, lipid profile, and body weight variation of rats.
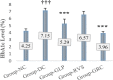
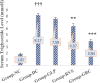
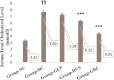
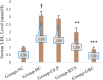
Results: This study's outcomes suggested that the combination therapy showed more statistically significant effect on blood glucose level, HbA1c level, lipid profile, and body weight variation than any single therapy. While the glimepiride monotherapy showed a statistically considerable effect on blood glucose level, HbA1c level, and body weight variation, the rosuvastatin treated group gave statistically non-significant effect on these parameters except body weight variation, which was found as downward trend. In addition, the rosuvastatin treated group showed a healthy lipid profile compared to glimepiride treated group.
Conclusions: Concluding the results of this study, it can be said that the treatment of glimepiride in combination with rosuvastatin may be more efficacious than monotherapy for preventing diabetes in rats with dyslipidemia.
Keywords: Alloxan; Cardiovascular disease; Combination therapy; Diabetes; Dyslipidemia; Hyperglycemia.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic interaction of losartan with glimepiride-metformin combination in rats and rabbits.Indian J Pharmacol. 2021 Nov-Dec;53(6):465-470. doi: 10.4103/ijp.IJP_845_19. Indian J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34975134 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic interactions between glimepiride and rosuvastatin in healthy Korean subjects: does the SLCO1B1 or CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism affect these drug interactions?Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017 Feb 23;11:503-512. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S129586. eCollection 2017. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017. PMID: 28260863 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Ethanolic Leaf Extract of Senna Fistula on some Haematological Parameters, Lipid Profile and Oxidative Stress in Alloxan-induced Diabetic Rats.Niger J Physiol Sci. 2015 Dec 20;30(1-2):87-93. Niger J Physiol Sci. 2015. PMID: 27507782
-
Improved glycaemic control by addition of glimepiride to metformin monotherapy in type 2 diabetic patients.Diabet Med. 2001 Oct;18(10):828-34. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2001.00582.x. Diabet Med. 2001. PMID: 11678974 Clinical Trial.
-
Repaglinide : a pharmacoeconomic review of its use in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Pharmacoeconomics. 2004;22(6):389-411. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200422060-00005. Pharmacoeconomics. 2004. PMID: 15099124 Review.
Cited by
-
Polyherbal extract improves glycometabolic control in alloxan-induced diabetic rats via down-regulating the MAPK/JNK pathway, modulating Nrf-2/Keap-1 expression, and stimulating insulin signaling.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(2):170-179. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.72553.15780. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38234664 Free PMC article.
-
Fluoxetine Treatment Decreases Cardiac Vagal Input and Alters the Serotonergic Modulation of the Parasympathetic Outflow in Diabetic Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 20;23(10):5736. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105736. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628547 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kennedy MSN, Masharani U. Pancreatic Hormones & Antidiabetic Drugs. In: Katzung BG, editor. Basic Clin Pharmacol a LANGE Med B. 14th ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2018. p. 747–771.
-
- Philipson LH, Steiner DF. Pas de deux or more: The sulfonylurea receptor and K+ channels. Science. 1995;268:372–3. - PubMed
-
- Massi-Benedetti M. Glimepiride in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review of the worldwide therapeutic experience. Clin Ther. 2003;25:799–816. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

