Ethanol Extract of Amomum tsao-ko Ameliorates Ovariectomy-Induced Trabecular Loss and Fat Accumulation
- PMID: 33546367
- PMCID: PMC7913548
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26040784
Ethanol Extract of Amomum tsao-ko Ameliorates Ovariectomy-Induced Trabecular Loss and Fat Accumulation
Abstract
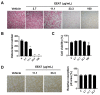
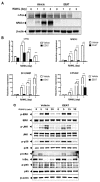
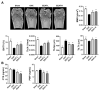
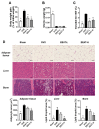
In Asia, Amomum tsao-ko has long been used as a spice or seasoning in food to stimulate digestion. In the present study, we evaluated the effects of ethanol extract of Amomum tsao-ko (EEAT) on menopausal osteoporosis and obesity. After the administration of EEAT in ovariectomy (OVX) mice models for five weeks, microcomputed tomography and a histological analysis were performed to assess, respectively, the trabecular structure and the fat accumulation in adipose, liver, and bone tissues. We also examined the effects of EEAT on a bone marrow macrophage model of osteoclastogenesis by in vitro stimulation from the receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa Β ligand (RANKL) through real-time PCR and Western blot analysis. In addition, ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) with authentic standards was applied to characterize the phytochemical profiling of EEAT. We found that EEAT significantly decreased OVX-induced body weight gain and fat accumulation, significantly prevented OVX-induced deterioration of bone mineral density and microstructure of trabecular tissues, and significantly inhibited osteoclast differentiation by downregulating NF-κB/Fos/NFATc1 signaling in osteoclasts. Furthermore, UHPLC-MS/MS identified eight beneficial phytochemicals in EEAT. Collectively, these results suggest that EEAT might be an effective nutraceutical candidate to attenuate menopausal osteoporosis by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and to prevent obesity by suppressing fat accumulation.
Keywords: Amomum tsao-ko; osteoclast differentiation; osteoporosis; ovariectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Water Extract of Lysimachia christinae Inhibits Trabecular Bone Loss and Fat Accumulation in Ovariectomized Mice.Nutrients. 2020 Jun 29;12(7):1927. doi: 10.3390/nu12071927. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32610585 Free PMC article.
-
Water Extract of Fritillariae thunbergii Bulbus Inhibits RANKL-Mediated Osteoclastogenesis and Ovariectomy-Induced Trabecular Bone Loss.Molecules. 2021 Dec 28;27(1):169. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010169. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 35011398 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Osteoporotic and Anti-Adipogenic Effects of the Water Extract of Drynaria roosii Nakaike in Ovariectomized Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet.Molecules. 2019 Aug 22;24(17):3051. doi: 10.3390/molecules24173051. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31443447 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanolic extract of Pyrrosia lingua (Thunb.) Farw. ameliorates OVX-induced bone loss and RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Mar;147:112640. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112640. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35033946
-
Health-promoting compounds in Amomum villosum Lour and Amomum tsao-ko: Fruit essential oil exhibiting great potential for human health.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 3;10(5):e27492. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27492. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38463888 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Chemical Changes during Maturation of Amomum tsao-ko Based on GC-MS, FT-NIR, and FT-MIR.ACS Omega. 2024 Jun 24;9(27):29857-29869. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c03717. eCollection 2024 Jul 9. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39005772 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization, Hypoglycemic Activity, and Antioxidant Activity of Methanol Extracts From Amomum tsao-ko: in vitro and in vivo Studies.Front Nutr. 2022 Jul 12;9:869749. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.869749. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35903449 Free PMC article.
-
Aging-related changes in metabolic indicators in female rats and their management with Tinospora cordifolia.Biogerontology. 2022 Jun;23(3):363-380. doi: 10.1007/s10522-022-09962-1. Epub 2022 Apr 30. Biogerontology. 2022. PMID: 35488997
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

