SPOCK, an R based package for high-throughput analysis of growth rate, survival, and chronological lifespan in yeast
- PMID: 33542965
- PMCID: PMC7857483
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tma.2020.08.003
SPOCK, an R based package for high-throughput analysis of growth rate, survival, and chronological lifespan in yeast
Abstract
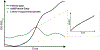
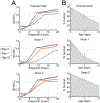
Plate reader-based methods for high-throughput measurement of growth rate, cellular survival, and chronological lifespan are a compelling addition to the already powerful toolbox of budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetics. These methods have overcome many of the limits of traditional yeast biology techniques, but also present a new bottleneck at the point of data-analysis. Herein, we describe SPOCK (Survival Percentage and Outgrowth Collection Kit), an R-based package for the analysis of data created by high-throughput plate reader based methods. This package allows for the determination of chronological lifespan, cellular growth rate, and survival in an efficient, robust, and reproducible fashion.
Keywords: R package; budding yeast; chronological lifespan; data-analysis; growth rate; high-throughput; software; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF COMPETING INTERESTS The authors do not have any conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

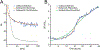
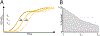
Similar articles
-
YODA: software to facilitate high-throughput analysis of chronological life span, growth rate, and survival in budding yeast.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Mar 18;11:141. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-141. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20298554 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid, high-throughput method for determining chronological lifespan in budding yeast.J Biol Methods. 2018 Dec 18;5(4):e106. doi: 10.14440/jbm.2018.272. eCollection 2018. J Biol Methods. 2018. PMID: 31453256 Free PMC article.
-
A Toolbox for Rapid Quantitative Assessment of Chronological Lifespan and Survival in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Traffic. 2016 Jun;17(6):689-703. doi: 10.1111/tra.12391. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Traffic. 2016. PMID: 26939796
-
Mechanisms that Link Chronological Aging to Cellular Quiescence in Budding Yeast.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 2;21(13):4717. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134717. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32630624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Communications between Mitochondria, the Nucleus, Vacuoles, Peroxisomes, the Endoplasmic Reticulum, the Plasma Membrane, Lipid Droplets, and the Cytosol during Yeast Chronological Aging.Front Genet. 2016 Sep 27;7:177. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00177. eCollection 2016. Front Genet. 2016. PMID: 27729926 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glucosylglycerol and proline reverse the effects of glucose on Rhodosporidium toruloides lifespan.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Mar 28;206(4):195. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-03930-8. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38546876
-
Multiomics of GCN4-Dependent Replicative Lifespan Extension Models Reveals Gcn4 as a Regulator of Protein Turnover in Yeast.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 10;24(22):16163. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216163. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003352 Free PMC article.
-
Glucosylglycerol Extends Chronological Lifespan of the Budding Yeast via an Increased Osmolarity Response.Indian J Microbiol. 2023 Mar;63(1):42-49. doi: 10.1007/s12088-023-01055-y. Epub 2023 Jan 9. Indian J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37188237 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous glucosylglycerol and proline extend the chronological lifespan of Rhodosporidium toruloides.Int Microbiol. 2023 Nov;26(4):807-819. doi: 10.1007/s10123-023-00336-2. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Int Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36786919
-
Aging, longevity, and the role of environmental stressors: a focus on wildfire smoke and air quality.Front Toxicol. 2023 Oct 11;5:1267667. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2023.1267667. eCollection 2023. Front Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37900096 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sherman F, Getting started with yeast, Methods in Enzymology. 350 (2002) 3–41. - PubMed
-
- Mikami Y, Scalarone GM, Kurita N, Yazawa K, Miyaji M, Comparative Studies on the Postantifungal Effect of Cispentacin and Pradimicin (BMY-28864) on Candida albicans, J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 33 (1992) 355–360. 10.3314/jjmm.33.355. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
