Effective Activation by Kynurenic Acid and Its Aminoalkylated Derivatives on M-Type K+ Current
- PMID: 33525680
- PMCID: PMC7865226
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22031300
Effective Activation by Kynurenic Acid and Its Aminoalkylated Derivatives on M-Type K+ Current
Abstract
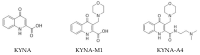
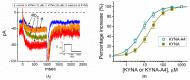
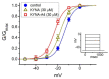
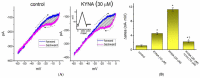
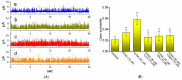
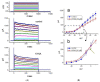
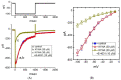
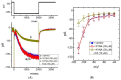
Kynurenic acid (KYNA, 4-oxoquinoline-2-carboxylic acid), an intermediate of the tryptophan metabolism, has been recognized to exert different neuroactive actions; however, the need of how it or its aminoalkylated amide derivative N-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)-3-(morpholinomethyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-2-carboxamide (KYNA-A4) exerts any effects on ion currents in excitable cells remains largely unmet. In this study, the investigations of how KYNA and other structurally similar KYNA derivatives have any adjustments on different ionic currents in pituitary GH3 cells and hippocampal mHippoE-14 neurons were performed by patch-clamp technique. KYNA or KYNA-A4 increased the amplitude of M-type K+ current (IK(M)) and concomitantly enhanced the activation time course of the current. The EC50 value required for KYNA- or KYNA-A4 -stimulated IK(M) was yielded to be 18.1 or 6.4 μM, respectively. The presence of KYNA or KYNA-A4 shifted the relationship of normalized IK(M)-conductance versus membrane potential to more depolarized potential with no change in the gating charge of the current. The voltage-dependent hysteretic area of IK(M) elicited by long-lasting triangular ramp pulse was observed in GH3 cells and that was increased during exposure to KYNA or KYNA-A4. In cell-attached current recordings, addition of KYNA raised the open probability of M-type K+ channels, along with increased mean open time of the channel. Cell exposure to KYNA or KYNA-A4 mildly inhibited delayed-rectifying K+ current; however, neither erg-mediated K+ current, hyperpolarization-activated cation current, nor voltage-gated Na+ current in GH3 cells was changed by KYNA or KYNA-A4. Under whole-cell, current-clamp recordings, exposure to KYNA or KYNA-A4 diminished the frequency of spontaneous action potentials; moreover, their reduction in firing frequency was attenuated by linopirdine, yet not by iberiotoxin or apamin. In hippocampal mHippoE-14 neurons, the addition of KYNA also increased the IK(M) amplitude effectively. Taken together, the actions presented herein would be one of the noticeable mechanisms through which they modulate functional activities of excitable cells occurring in vivo.
Keywords: M-type K+ current; action potential; hippocampal neuron; kynurenic acid; kynurenic acid derivative; pituitary cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
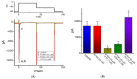
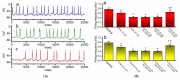
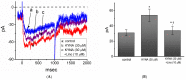
Similar articles
-
Effective Perturbations by Small-Molecule Modulators on Voltage-Dependent Hysteresis of Transmembrane Ionic Currents.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 21;23(16):9453. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169453. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effectiveness in Activating M-Type K+ Current Produced by Solifenacin ([(3R)-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-yl] (1S)-1-phenyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinoline-2-carboxylate): Independent of Its Antimuscarinic Action.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 17;22(22):12399. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212399. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830281 Free PMC article.
-
Concerted suppression of Ih and activation of IK(M) by ivabradine, an HCN-channel inhibitor, in pituitary cells and hippocampal neurons.Brain Res Bull. 2019 Jul;149:11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.03.016. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Brain Res Bull. 2019. PMID: 30951796
-
Characterization of Effectiveness in Concerted Ih Inhibition and IK(Ca) Stimulation by Pterostilbene (Trans-3,5-dimethoxy-4'-hydroxystilbene), a Stilbenoid.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 5;21(1):357. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010357. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31948124 Free PMC article.
-
Kynurenic Acid Acts as a Signaling Molecule Regulating Energy Expenditure and Is Closely Associated With Metabolic Diseases.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 24;13:847611. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.847611. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35282457 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effective Perturbations of the Amplitude, Gating, and Hysteresis of IK(DR) Caused by PT-2385, an HIF-2α Inhibitor.Membranes (Basel). 2021 Aug 17;11(8):636. doi: 10.3390/membranes11080636. Membranes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34436399 Free PMC article.
-
Effective Perturbations by Small-Molecule Modulators on Voltage-Dependent Hysteresis of Transmembrane Ionic Currents.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 21;23(16):9453. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169453. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence for Dual Activation of IK(M) and IK(Ca) Caused by QO-58 (5-(2,6-Dichloro-5-fluoropyridin-3-yl)-3-phenyl-2-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazolol[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-one).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 24;23(13):7042. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137042. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806047 Free PMC article.
-
The Effectiveness in Activating M-Type K+ Current Produced by Solifenacin ([(3R)-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-yl] (1S)-1-phenyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinoline-2-carboxylate): Independent of Its Antimuscarinic Action.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 17;22(22):12399. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212399. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830281 Free PMC article.
-
Tryptophan Challenge in Healthy Controls and People with Schizophrenia: Acute Effects on Plasma Levels of Kynurenine, Kynurenic Acid and 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Aug 15;15(8):1003. doi: 10.3390/ph15081003. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hilmas C., Pereira E.F., Alkondon M., Rassoulpour A., Schwarcz R., Albuquerque E.X. The brain metabolite kynurenic acid inhibits alpha7 nicotinic receptor activity and increases non-alpha7 nicotinic receptor expression: Physiopathological implications. J. Neurosci. 2001;21:7463–7473. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-19-07463.2001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

