Toxicological Consequences of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles (TiO2NPs) and Their Jeopardy to Human Population
- PMID: 33520589
- PMCID: PMC7835448
- DOI: 10.1007/s12668-021-00836-3
Toxicological Consequences of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles (TiO2NPs) and Their Jeopardy to Human Population
Abstract
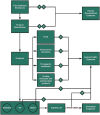
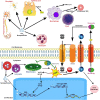
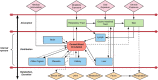
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) are the most produced nanomaterial for food additives, pigments, photocatalysis, and personal care products. These nanomaterials are at the forefront of rapidly developing indispensable nanotechnology. In all these nanomaterials, titanium dioxide (TiO2) is the most common nanomaterial which is being synthesized for many years. These nanoparticles of TiO2 are widely used at the commercial level, especially in cosmetic industries. High usage in such a way has increased the toxicological consequences of the human population. Several studies have shown that TiO2 NPs accumulated after oral exposure or inhalation in the alimentary canal, lungs, heart, liver, spleen, cardiac muscle, and kidneys. Additionally, in mice and rats, they disturb glucose and lipid homeostasis. Moreover, TiO2 nanoparticles primarily cause adverse reactions by inducing oxidative stress that leads to cell damage, inflammation, genotoxicity, and adverse immune responses. The form and level of destruction are strongly based on the physical and chemical properties of TiO2 nanoparticles, which administer their reactivity and bioavailability. Studies give indications that TiO2 NPs cause both DNA strand breaks and chromosomal damages. The effects of genotoxicity do not depend only on particle surface changes, size, and exposure route, but also relies on the duration of exposure. Most of these effects may be because of a very high dose of TiO2 NPs. Despite increased production and use, epidemiological data for TiO2 NPs is still missing. This review discusses previous research regarding the impact of TiO2 NP toxicity on human health and highlights areas that require further understanding in concern of jeopardy to the human population. This review is important to point out areas where extensive research is needed; thus, their possible impact on individual health should be investigated in more details.
Keywords: Jeopardy; Nanomaterials; Nanoparticles; Nanotechnology; TiO2; Titanium dioxide nanoparticles.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC part of Springer Nature 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Exposure on Human Health-a Review.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020 Jan;193(1):118-129. doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-01706-6. Epub 2019 Apr 13. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020. PMID: 30982201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral toxicological study of titanium dioxide nanoparticles with a crystallite diameter of 6 nm in rats.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2023 Jun 20;20(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12989-023-00533-x. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37340415 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in genotoxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in vivo and in vitro.NanoImpact. 2022 Jan;25:100377. doi: 10.1016/j.impact.2021.100377. Epub 2021 Dec 17. NanoImpact. 2022. PMID: 35559883 Review.
-
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: a review of current toxicological data.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2013 Apr 15;10:15. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-10-15. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23587290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of titanium dioxide nanoparticles with glucose on young rats after oral administration.Nanomedicine. 2015 Oct;11(7):1633-42. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2015.06.002. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Nanomedicine. 2015. PMID: 26115638
Cited by
-
Characterization of Food-Additive Titanium Dioxide and Dietary Exposure to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles among the Chinese Population.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Aug 31;14(17):1427. doi: 10.3390/nano14171427. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39269089 Free PMC article.
-
A review of multilayer and composite films and coatings for active biodegradable packaging.NPJ Sci Food. 2022 Mar 11;6(1):18. doi: 10.1038/s41538-022-00132-8. NPJ Sci Food. 2022. PMID: 35277514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on Human Health and the Environment.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Sep 10;11(9):2354. doi: 10.3390/nano11092354. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34578667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on Chick Embryo: Immunomodulatory, Hepatic and Biochemical Alterations.Vet Med Sci. 2024 Nov;10(6):e70105. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70105. Vet Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39474769 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of genomic and mitochondrial DNA integrity in the renal tissue of mice administered with acrylamide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 19;13(1):13523. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40676-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37598254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khan I, Saeed K, & Khan I. (2019). Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arabian Journal of Chemistry,12(7), 908–931.
-
- Saehana S, Prasetyowati R, Hidayat MI, Arifin P, Khairurrijal A. Efficiency improvement in TiO2-particle based solar cells after deposition of metal in spaces between particles. International Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. 2011;12:15.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
