Neurolysin substrates bradykinin, neurotensin and substance P enhance brain microvascular permeability in a human in vitro model
- PMID: 33506602
- PMCID: PMC8166215
- DOI: 10.1111/jne.12931
Neurolysin substrates bradykinin, neurotensin and substance P enhance brain microvascular permeability in a human in vitro model
Abstract
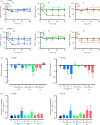
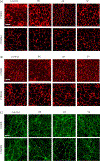
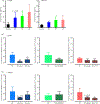
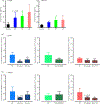
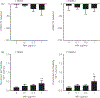
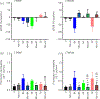
Increased brain microvascular permeability and disruption of blood-brain barrier (BBB) function are among hallmarks of several acute neurodegenerative disorders, including stroke. Numerous studies suggest the involvement of bradykinin (BK), neurotensin (NT) and substance P (SP) in BBB impairment and oedema formation after stroke; however, there is paucity of data in regard to the direct effects of these peptides on the brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs) and BBB. The present study aimed to evaluate the direct effects of BK, NT and SP on the permeability of BBB in an in vitro model based on human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived BMECs. Our data indicate that all three peptides increase BBB permeability in a concentration-dependent manner in an in vitro model formed from two different iPSC lines (CTR90F and CTR65M) and widely used hCMEC/D3 human BMECs. The combination of BK, NT and SP at a sub-effective concentration also resulted in increased BBB permeability in the iPSC-derived model indicating potentiation of their action. Furthermore, we observed abrogation of BK, NT and SP effects with pretreatment of pharmacological blockers targeting their specific receptors. Additional mechanistic studies indicate that the short-term effects of these peptides are not mediated through alteration of tight-junction proteins claudin-5 and occludin, but likely involve redistribution of F-actin and secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor. This is the first experimental study to document the increased permeability of the BBB in response to direct action of NT in an in vitro model. In addition, our study confirms the expected but not well-documented, direct effect of SP on BBB permeability and adds to the well-recognised actions of BK on BBB. Lastly, we demonstrate that peptidase neurolysin can neutralise the effects of these peptides on BBB, suggesting potential therapeutic implications.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier; microvascular permeability; neuropeptide; oedema formation; peptidase neurolysin.
© 2021 British Society for Neuroendocrinology.
Figures
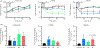
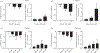
Similar articles
-
Bradykinin/bradykinin 1 receptor promotes brain microvascular endothelial cell permeability and proinflammatory cytokine release by downregulating Wnt3a.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2022 Dec;36(12):e23213. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23213. Epub 2022 Sep 16. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36111657 Free PMC article.
-
The proinflammatory peptide substance P promotes blood-brain barrier breaching by breast cancer cells through changes in microvascular endothelial cell tight junctions.Int J Cancer. 2014 Mar 1;134(5):1034-44. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28433. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Int J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 23934616
-
Ligustilide Ameliorates the Permeability of the Blood-Brain Barrier Model In Vitro During Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation Injury Through HIF/VEGF Pathway.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2019 May;73(5):316-325. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000664. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30855407
-
The development of the bradykinin agonist labradimil as a means to increase the permeability of the blood-brain barrier: from concept to clinical evaluation.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2001;40(2):105-23. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200140020-00003. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2001. PMID: 11286321 Review.
-
Models of the blood-brain barrier using iPSC-derived cells.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2020 Sep;107:103533. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2020.103533. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32717317 Review.
Cited by
-
Potentials of Neuropeptides as Therapeutic Agents for Neurological Diseases.Biomedicines. 2022 Feb 1;10(2):343. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020343. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35203552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bradykinin-target therapies in SARS-CoV-2 infection: current evidence and perspectives.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022 Mar;395(3):275-283. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02206-6. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35089406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular metabolism of substance P produces neurokinin-1 receptor peptide agonists with diminished cyclic AMP signaling.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Jul 1;327(1):C151-C167. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00103.2024. Epub 2024 May 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38798270
-
Discovery of the Next Generation of Non-peptidomimetic Neurolysin Activators with High Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability: a Pharmacokinetics Study in Healthy and Stroke Animals.Pharm Res. 2023 Nov;40(11):2747-2758. doi: 10.1007/s11095-023-03619-5. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Pharm Res. 2023. PMID: 37833570
-
The Role of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in the Treatment of Stroke.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024;22(14):2368-2383. doi: 10.2174/1570159X22666240603084558. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39403058 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2018 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137:e67–e492. - PubMed
-
- Yang Y, Estrada EY, Thompson JF, Liu W, Rosenberg GA. Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated disruption of tight junction proteins in cerebral vessels is reversed by synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor in focal ischemia in rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007;27:697–709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

