MicroRNA-193a-5p Regulates the Synthesis of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids by Targeting Fatty Acid Desaturase 1 (FADS1) in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells
- PMID: 33504005
- PMCID: PMC7911131
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11020157
MicroRNA-193a-5p Regulates the Synthesis of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids by Targeting Fatty Acid Desaturase 1 (FADS1) in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells
Abstract
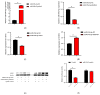
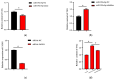
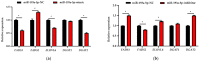
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are seriously threatening to human life and health. Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are known for their role in preventing CVDs. It is beneficial to population health to promote the content of PUFAs in bovine milk. In recent years, limited research based on molecular mechanisms has focused on this field. The biological roles of numerous microRNAs (miRNAs) remain unknown. In this study, a promising and negatively correlated pair of the miRNA (miRNA-193a-5p) and a fatty acid desaturase 1 (FADS1) gene are identified and screened to explore whether they are potential factors of PUFAs' synthesis in bovine milk. The targeted relationship between miRNA-193a-5p and FADS1 in bovine mammary epithelial cells (BMECs) is demonstrated by dual luciferase reporter assays. qRT-PCR and western blot assays indicate that both the expression of mRNA and the protein FADS1 show a negative correlation with miRNA-193a-5p expression in BMECs. Also, miR-193a-5p expression is positively correlated with the expression of genes associated with milk fatty acid metabolism, including ELOVL fatty acid elongase 6 (ELOVL6) and diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2 (DGAT2). The expression of fatty acid desaturase 2 (FADS2) is negatively correlated with miR-193a-5p expression in BMECs. The contents of triglycerides (TAG), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosapentaenoic acid (DPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) have a significant positive correlation with the expression of FADS1 and a significant negative correlation with the expression of miR-193a-5p in BMECs. For the first time, this study confirms that miRNA-193a-5p regulates PUFAs metabolism in BMECs by targeting FADS1, indicating that miRNA-193a-5p and FADS1 are underlying factors that improve PUFAs content in bovine milk.
Keywords: FADS1; MicroRNA-193a-5p; bovine mammary epithelial cells; bovine milk; polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

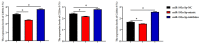

Similar articles
-
MiR-16a Regulates Milk Fat Metabolism by Targeting Large Tumor Suppressor Kinase 1 (LATS1) in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells.J Agric Food Chem. 2019 Oct 9;67(40):11167-11178. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b04883. Epub 2019 Sep 30. J Agric Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 31542928
-
Goat FADS2 controlling fatty acid metabolism is directly regulated by SREBP1 in mammary epithelial cells.J Anim Sci. 2023 Jan 3;101:skad030. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad030. J Anim Sci. 2023. PMID: 36694375 Free PMC article.
-
miR-497 regulates fatty acid synthesis via LATS2 in bovine mammary epithelial cells.Food Funct. 2020 Oct 21;11(10):8625-8636. doi: 10.1039/d0fo00952k. Food Funct. 2020. PMID: 32935676
-
A mathematical model for mammary fatty acid synthesis and triglyceride assembly: the role of stearoyl CoA desaturase (SCD).J Dairy Res. 2004 Nov;71(4):385-97. doi: 10.1017/s0022029904000354. J Dairy Res. 2004. PMID: 15605704 Review.
-
Genetically determined variation in polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism may result in different dietary requirements.Nestle Nutr Workshop Ser Pediatr Program. 2008;62:35-44; discussion 44-9. doi: 10.1159/000146246. Nestle Nutr Workshop Ser Pediatr Program. 2008. PMID: 18626191 Review.
Cited by
-
Malonyl/Acetyltransferase (MAT) Knockout Decreases Triacylglycerol and Medium-Chain Fatty Acid Contents in Goat Mammary Epithelial Cells.Foods. 2022 Apr 29;11(9):1291. doi: 10.3390/foods11091291. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35564013 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-199a-3p regulates proliferation and milk fat synthesis of ovine mammary epithelial cells by targeting VLDLR.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Aug 5;9:948873. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.948873. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35990270 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of microRNAs in the Mammary Gland Development, Health, and Function of Cattle, Goats, and Sheep.Noncoding RNA. 2021 Dec 13;7(4):78. doi: 10.3390/ncrna7040078. Noncoding RNA. 2021. PMID: 34940759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in epigenetic regulation of milk synthesis, with particular emphasis on mRNA regulation and DNA methylation.Cell Cycle. 2023 Jul-Aug;22(14-16):1675-1693. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2023.2225939. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Cell Cycle. 2023. PMID: 37409592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous determination of cis- and trans-palmitoleic acid in rat serum by UPLC-MS/MS.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 5;12(1):16637. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20739-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36198714 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31872324/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- BK20190881/Basic Research Program of Jiangsu Province
- 2019M650126/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- 19KJB230001/Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China
- JATS (2019) 446/Jiangsu Modern Dairy Industry Technology System
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

