Fetuin-A is a HIF target that safeguards tissue integrity during hypoxic stress
- PMID: 33483479
- PMCID: PMC7822914
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-20832-7
Fetuin-A is a HIF target that safeguards tissue integrity during hypoxic stress
Abstract
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) is associated with reduced kidney size at birth, accelerated renal function decline, and increased risk for chronic kidney and cardiovascular diseases in adults. Precise mechanisms underlying fetal programming of adult diseases remain largely elusive and warrant extensive investigation. Setting up a mouse model of hypoxia-induced IUGR, fetal adaptations at mRNA, protein and cellular levels, and their long-term functional consequences are characterized, using the kidney as a readout. Here, we identify fetuin-A as an evolutionary conserved HIF target gene, and further investigate its role using fetuin-A KO animals and an adult model of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Beyond its role as systemic calcification inhibitor, fetuin-A emerges as a multifaceted protective factor that locally counteracts calcification, modulates macrophage polarization, and attenuates inflammation and fibrosis, thus preserving kidney function. Our study paves the way to therapeutic approaches mitigating mineral stress-induced inflammation and damage, principally applicable to all soft tissues.
Conflict of interest statement
The University of Bern has filed a European patent on behalf of U.H.-D. and S. Rudloff with application number: EP20162490. The patent relates to use of fetuin-A in treating renal disorders. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
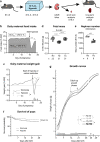
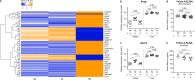
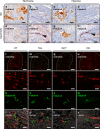

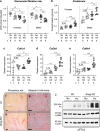

Similar articles
-
Tissue chaperoning-the expanded functions of fetuin-A beyond inhibition of systemic calcification.Pflugers Arch. 2022 Aug;474(8):949-962. doi: 10.1007/s00424-022-02688-6. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Pflugers Arch. 2022. PMID: 35403906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microvasculopathy and soft tissue calcification in mice are governed by fetuin-A, magnesium and pyrophosphate.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 19;15(2):e0228938. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228938. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32074140 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical implications of fetuin-A.Adv Clin Chem. 2019;89:79-130. doi: 10.1016/bs.acc.2018.12.003. Epub 2019 Feb 8. Adv Clin Chem. 2019. PMID: 30797472 Review.
-
Endothelial HIF-2 mediates protection and recovery from ischemic kidney injury.J Clin Invest. 2014 Jun;124(6):2396-409. doi: 10.1172/JCI69073. Epub 2014 May 1. J Clin Invest. 2014. PMID: 24789906 Free PMC article.
-
Lumenal calcification and microvasculopathy in fetuin-A-deficient mice lead to multiple organ morbidity.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 19;15(2):e0228503. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228503. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32074120 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
NR4A2 may be a potential diagnostic biomarker for myocardial infarction: A comprehensive bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 22;13:1061800. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1061800. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36618351 Free PMC article.
-
17α-estradiol, a lifespan-extending compound, attenuates liver fibrosis by modulating collagen turnover rates in male mice.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Feb 1;324(2):E120-E134. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00256.2022. Epub 2022 Dec 14. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 36516471 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational modifications glycosylation and phosphorylation of the major hepatic plasma protein fetuin-A are associated with CNS inflammation in children.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 7;17(10):e0268592. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268592. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36206263 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue chaperoning-the expanded functions of fetuin-A beyond inhibition of systemic calcification.Pflugers Arch. 2022 Aug;474(8):949-962. doi: 10.1007/s00424-022-02688-6. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Pflugers Arch. 2022. PMID: 35403906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased UHMWPE Particle-Induced Osteolysis in Fetuin-A-Deficient Mice.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Jan 4;14(1):30. doi: 10.3390/jfb14010030. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 36662077 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reyes, L. & Mañalich, R. Long-term consequences of low birth weight. Kidney Int. Suppl, 68, S107–S111 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

