Targeting the integrated stress response in ophthalmology
- PMID: 33474991
- PMCID: PMC8292453
- DOI: 10.1080/02713683.2020.1867748
Targeting the integrated stress response in ophthalmology
Abstract
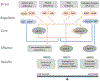
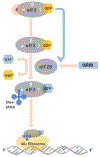
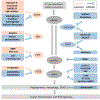
Purpose: To summarize the Integrated Stress Response (ISR) in the context of ophthalmology, with special interest on the cornea and anterior segment. Results: The ISR is a powerful and conserved signaling pathway that allows for cells to respond to a diverse array of both intracellular and extracellular stressors. The pathway is classically responsible for coordination of the cellular response to amino acid starvation, ultraviolet light, heme dysregulation, viral infection, and unfolded protein. Under normal circumstances, it is considered pro-survival and a necessary mechanism through which protein translation is controlled. However, in cases of severe or prolonged stress the pathway can promote apoptosis, and loss of normal cellular phenotype. The activation of this pathway culminates in the global inhibition of cap-dependent protein translation and the canonical expression of the activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4). Conclusion:The eye is uniquely exposed to ISR responsive stressors due to its environmental exposure and relative isolation from the circulatory system which are necessary for its function. We will discuss how this pathway is critical for the proper function of the tissue, its role in development, as well as how targeting of the pathway could alleviate key aspects of diverse ophthalmic diseases.
Keywords: ATF4; ISR; isrib, cornea; eIF2.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest:
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ATF4 and the integrated stress response are induced by ethanol and cytochrome P450 2E1 in human hepatocytes.J Hepatol. 2011 Apr;54(4):729-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.07.023. Epub 2010 Sep 29. J Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21146245
-
Integrated Stress Response (ISR) Pathway: Unraveling Its Role in Cellular Senescence.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 13;24(24):17423. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417423. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Sulfur Amino Acid Restriction and the Integrated Stress Response: Mechanistic Insights.Nutrients. 2019 Jun 15;11(6):1349. doi: 10.3390/nu11061349. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31208042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Both transcriptional regulation and translational control of ATF4 are central to the integrated stress response.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 22;285(43):33165-33174. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.167213. Epub 2010 Aug 23. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20732869 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive Protein Translation by the Integrated Stress Response Maintains the Proliferative and Migratory Capacity of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2019 Dec;17(12):2343-2355. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-19-0245. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Mol Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31551255 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Roles of interacting stress-related genes in lifespan regulation: insights for translating experimental findings to humans.J Transl Genet Genom. 2021;5(4):357-379. Epub 2021 Oct 19. J Transl Genet Genom. 2021. PMID: 34825130 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide RNA Sequencing of Human Trabecular Meshwork Cells Treated with TGF-β1: Relevance to Pseudoexfoliation Glaucoma.Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 15;12(11):1693. doi: 10.3390/biom12111693. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36421707 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of the integrated stress response in the rat cornea.Exp Eye Res. 2021 Sep;210:108722. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108722. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Exp Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 34370978 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Integrated Stress Response in Cancer Therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 24;12:747837. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.747837. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34630117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated Stress Response Regulation of Corneal Epithelial Cell Motility and Cytokine Production.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022 Jul 8;63(8):1. doi: 10.1167/iovs.63.8.1. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 35802384 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ye J, Kumanova M, Hart LS, Sloane K, Zhang H, De Panis DN, Bobrovnikova-Marjon E, Diehl JA, Ron D, Koumenis C. The GCN2-ATF4 pathway is critical for tumour cell survival and proliferation in response to nutrient deprivation. EMBO J. 2010;29(12):2082–2096. doi:10.1038/emboj.2010.81. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
