Effect of mannose-binding lectin gene polymorphisms on the risk of rheumatoid arthritis: Evidence from a meta-analysis
- PMID: 33458965
- PMCID: PMC7986746
- DOI: 10.1111/1756-185X.14060
Effect of mannose-binding lectin gene polymorphisms on the risk of rheumatoid arthritis: Evidence from a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The effect of mannose-binding lectin (MBL) gene polymorphisms on susceptibility of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) were evaluated in ethnically different populations, whereas the results were always inconsistent.
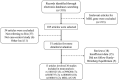
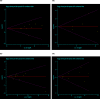
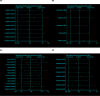
Materials and methods: Fourteen articles involving 36 datasets were recruited to evaluate the association between MBL gene polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis in a meta-analysis. The random or fixed effect models were used to evaluate the pooled odds ratios (ORs) and their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results: Stratified analysis by ethnicities was conducted and the result revealed that rs1800450 (T vs C, OR = 1.32, 95% CI: 1.04-1.67, P < .05) and MBL-A/O (T vs C, OR = 1.20, 95% CI: 1.08-1.34, P < .001) were strongly associated with RA in Brazilian populations. In addition, the significant relationship between rs11003125 (T vs C, OR = 1.16, 95% CI: 1.06-1.26, P < .05) with RA were also observed in East Asian populations. Meanwhile, the inverse associations between rs5030737 with RA in East Asians and rs1800450 with RA in Indians were acquired. However, no association between any MBL polymorphism with RA susceptibility was confirmed in Caucasians.
Conclusions: The structural polymorphisms in exon 1 of MBL gene may significantly contribute to susceptibility and development of RA in Brazilian and Indian populations, whereas the functional polymorphisms in the promoter region were more likely to associate with RA in East Asians.
Keywords: mannose-binding lectin; meta-analysis; polymorphism; rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2021 The Authors. International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases published by Asia Pacific League of Associations for Rheumatology and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Meta-analysis of functional MBL polymorphisms. Associations with rheumatoid arthritis and primary Sjögren's syndrome.Z Rheumatol. 2014 Sep;73(7):657-64. doi: 10.1007/s00393-014-1408-x. Z Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 25060516
-
Mannose-binding lectin polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis: A short review and meta-analysis.Mol Immunol. 2016 Jan;69:77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.10.010. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Mol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26608926 Review.
-
Mannan Binding Lectin (MBL) genotypes coding for high MBL serum levels are associated with rheumatoid factor negative rheumatoid arthritis in never smokers.Arthritis Res Ther. 2011 Apr 15;13(2):R65. doi: 10.1186/ar3321. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011. PMID: 21496252 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the presence of mannose-binding lectin polymorphisms on the occurrence of leishmaniasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.An Bras Dermatol. 2022 May-Jun;97(3):298-306. doi: 10.1016/j.abd.2021.08.004. Epub 2022 Mar 21. An Bras Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35331599 Free PMC article.
-
Association of MBL2 gene polymorphisms and systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility: A meta-analysis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2021 Feb;24(2):147-158. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.14017. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Int J Rheum Dis. 2021. PMID: 33146461 Review.
Cited by
-
A Nanoplasmonic Assay for Point-of-Care Detection of Mannose-Binding Lectin in Human Serum.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Jun 12;16(23):30556-30566. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c04018. Epub 2024 May 28. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38806166 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Transcriptional Regulation of Glycolysis in Circulating CD8+ T Cells of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jul 7;13(7):1216. doi: 10.3390/genes13071216. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35886000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calabresi E, Petrelli F, Bonifacio AF, et al. One year in review 2018: pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018;36(2):175‐184. - PubMed
-
- Daniel A, Smolen JS. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis. A review. JAMA. 2018;14(34):254‐261. - PubMed
-
- Bae SC, Lee YH. Causal association between body mass index and risk of rheumatoid arthritis: a Mendelian randomization study. Eur J Clin Invest. 2019;49(4):126‐138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

