High Monopolar Spindle 1 Is Associated with Short Survival of Cholangiocarcinoma Patients and Enhances the Progression Via AKT and STAT3 Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 33450849
- PMCID: PMC7828338
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9010068
High Monopolar Spindle 1 Is Associated with Short Survival of Cholangiocarcinoma Patients and Enhances the Progression Via AKT and STAT3 Signaling Pathways
Abstract
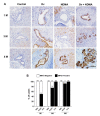
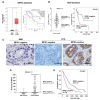
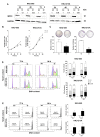
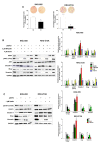
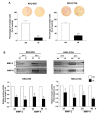
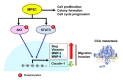
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a malignancy of the bile duct epithelium. The major problems of this cancer are late diagnosis and a high rate of metastasis. CCA patients in advanced stages have poor survival and cannot be cured with surgery. Therefore, targeting molecules involved in the metastatic process may be an effective CCA treatment. Monopolar spindle 1 (MPS1) is a kinase protein that controls the spindle assemble checkpoint in mitosis. It is overexpressed in proliferating cells and various cancers. The functional roles of MPS1 in CCA progression have not been investigated. The aims of this study were to examine the roles and molecular mechanisms of MPS1 in CCA progression. Immunohistochemistry results showed that MPS1 was up-regulated in carcinogenesis of CCA in a hamster model, and positive expression of MPS1 in human CCA tissues was correlated to short survival of CCA patients (n = 185). Small interfering RNA (siRNA)-induced knockdown of MPS1 expression reduced cell proliferation via G2/M arrest, colony formation, migration, and invasion. Moreover, MPS1 controlled epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT)-mediated migration via AKT and STAT3 signaling transductions. MPS1 was also involved in MMPs-dependent invasion of CCA cell lines. The current research highlights for the first time that MPS1 has an essential role in promoting the progression of CCA via AKT and STAT3 signaling pathways and could be an attractive target for metastatic CCA treatment.
Keywords: AKT; Cholangiocarcinoma; EMT; MMPs; MPS1; STAT3; invasion; migration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpression of BubR1 Mitotic Checkpoint Protein Predicts Short Survival and Influences the Progression of Cholangiocarcinoma.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 19;12(7):1611. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071611. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062183 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple actions of NMS-P715, the monopolar spindle 1 (MPS1) mitotic checkpoint inhibitor in liver fluke-associated cholangiocarcinoma cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2022 May 5;922:174899. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.174899. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35337815
-
Up-regulated LINC00261 predicts a poor prognosis and promotes a metastasis by EMT process in cholangiocarcinoma.Pathol Res Pract. 2020 Jan;216(1):152733. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.152733. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Pathol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 31812439
-
The novel epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related proteins and their therapeutic targets in cholangiocarcinoma: a narrative review.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023 Jun 30;14(3):1593-1612. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-1126. Epub 2023 May 26. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37435208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Therapeutic Implications of Co-Targeting the EGFR and Spindle Assembly Checkpoint Pathways in Oral Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Sep 11;16(9):1196. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16091196. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39339232 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of BubR1 Mitotic Checkpoint Protein Predicts Short Survival and Influences the Progression of Cholangiocarcinoma.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 19;12(7):1611. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071611. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062183 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

