Recent Advancement in Nanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery System Against Viral Infections
- PMID: 33447909
- PMCID: PMC7808403
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-020-01908-5
Recent Advancement in Nanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery System Against Viral Infections
Abstract
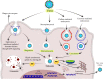
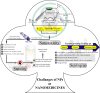
In the last few decades, the exponential rise in the incidence of viral infections sets a global health emergency across the world. The biomimetic architecture, the ability to hijack host immune responses, continuous antigen shifting, and drafting are the major critical factors that are responsible for the unavailability of a concrete therapeutic regimen against viral infections. Further, inappropriate pharmacodynamic physicochemical and biological parameters such as low aqueous solubility, poor permeability, high affinity for plasm proteins, short biological half-lives, and fast elimination from the systemic circulation are the major critical factors that govern the suboptimal drug concentration at the target site that leads to the development of drug resistance. To address this issue, nanotechnology-based drug delivery approach is emerged as an altering method to attain the optimal drug concentration at the target site for a prolonged period by integrating the nanoengineering tools in the synthesis of nanoparticles. Nanodimensional configuration with enhanced permeability and retention effect, increased surface-area-to-volume ratio, provision for surface functionalization, etc., are the privileged aspects that make it an effective drug delivery system for dispensing the antiviral therapeutics. However, size, shape, charge, and surface topology of nanoparticles are the greater influential factors that determine target-specific drug delivery, optimum cellular uptake, degree of opsonization by the host immune cells, drug retention time, transcytosis, the extension of biological half-life, in vivo stability, and cytotoxicity. The review will enlighten the elaborative role of nanotechnology-based drug delivery and the major challenging aspect of clinical safety and efficacy.
Keywords: antiviral; organic and inorganic nanocarrier system; pharmacokinetics; targeted delivery; therapeutic nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nanotechnology advances in pathogen- and host-targeted antiviral delivery: multipronged therapeutic intervention for pandemic control.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021 Aug;11(4):1420-1437. doi: 10.1007/s13346-021-00965-y. Epub 2021 Mar 21. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 33748879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicine formulations for the delivery of antiviral drugs: a promising solution for the treatment of viral infections.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2018 Jan;15(1):93-114. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2017.1360863. Epub 2017 Aug 3. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2018. PMID: 28749739
-
Drug Nanocrystals: A Delivery Channel for Antiviral Therapies.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Feb 17;25(3):41. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02754-5. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38366178 Review.
-
Nanoparticulate delivery systems for antiviral drugs.Antivir Chem Chemother. 2010;21(2):53-70. doi: 10.3851/IMP1684. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2010. PMID: 21107015 Review.
-
Nanotechnology in medicine revolutionizing drug delivery for cancer and viral infection treatments.Int J Pharm. 2024 Jul 20;660:124345. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124345. Epub 2024 Jun 15. Int J Pharm. 2024. PMID: 38885775 Review.
Cited by
-
An Overview of Supramolecular Platforms Boosting Drug Delivery.Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2023 Nov 13;2023:8608428. doi: 10.1155/2023/8608428. eCollection 2023. Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2023. PMID: 38028018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential use of bacteria and bacterial derivatives as drug delivery systems for viral infection.Virol J. 2023 Oct 3;20(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02183-z. Virol J. 2023. PMID: 37789431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metallic nanomaterials - targeted drug delivery approaches for improved bioavailability, reduced side toxicity, and enhanced patient outcomes.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2024 Apr-Jun;65(2):145-158. doi: 10.47162/RJME.65.2.01. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2024. PMID: 39020529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Highly active antiretroviral therapy conjugated silver nanoparticle ameliorates testicular injury in type-2 diabetic rats.Heliyon. 2021 Dec 9;7(12):e08580. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08580. eCollection 2021 Dec. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34917828 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Nanoparticles as Promising Carriers for mRNA Vaccines for Viral Lung Infections.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 3;15(4):1127. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041127. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111613 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

