Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2020: An Appraisal of Current Status
- PMID: 33434426
- PMCID: PMC7850879
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0254
Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2020: An Appraisal of Current Status
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate the recent prevalence, management, and comorbidities of diabetes among Korean adults aged ≥30 years by analyzing nationally representative data.
Methods: This study used data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2016 to 2018, and the percentage and total number of people ≥30 years of age with diabetes and impaired fasting glucose (IFG) were estimated.
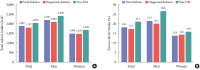
Results: In 2018, 13.8% of Korean adults aged ≥30 years had diabetes, and adults aged ≥65 years showed a prevalence rate of 28%. The prevalence of IFG was 26.9% in adults aged ≥30 years. From 2016 to 2018, 35% of the subjects with diabetes were not aware of their condition. Regarding comorbidities, 53.2% and 61.3% were obese and hypertensive, respectively, and 72% had hypercholesterolemia as defined by low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) ≥100 mg/dL in people with diabetes. Of the subjects with diabetes, 43.7% had both hypertension and hypercholesterolemia. With regard to glycemic control, only 28.3% reached the target level of <6.5%. Moreover, only 11.5% of subjects with diabetes met all three targets of glycosylated hemoglobin, blood pressure, and LDL-C. The percentage of energy intake from carbohydrates was higher in diabetes patients than in those without diabetes, while that from protein and fat was lower in subjects with diabetes.
Conclusion: The high prevalence and low control rate of diabetes and its comorbidities in Korean adults were confirmed. More stringent efforts are needed to improve the comprehensive management of diabetes to reduce diabetes-related morbidity and mortality.
Keywords: Comorbidity; Diabetes mellitus; Hypercholesterolemia; Hypertension; Prediabetic state; Prevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
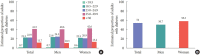
Similar articles
-
Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2018: An Appraisal of Current Status.Diabetes Metab J. 2019 Aug;43(4):487-494. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2019.0067. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Diabetes Metab J. 2019. PMID: 31339012 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea, 2016: An Appraisal of Current Status.Diabetes Metab J. 2018 Oct;42(5):415-424. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0017. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Diabetes Metab J. 2018. PMID: 30113146 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea 2021.Diabetes Metab J. 2022 May;46(3):417-426. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0106. Epub 2022 May 25. Diabetes Metab J. 2022. PMID: 35656565 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Current Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Korean Adults Based on Fact Sheets.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2020 Mar;35(1):85-94. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.85. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2020. PMID: 32207267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association.Diabetes Metab J. 2023 Sep;47(5):575-594. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0282. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Diabetes Metab J. 2023. PMID: 37793979 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ocular motility disorders following coronavirus disease-19 vaccination.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023 Apr;261(4):1127-1139. doi: 10.1007/s00417-022-05888-z. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36383278 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Glycosylated Hemoglobin Level and Cancer-Related Mortality in Patients without Diabetes.J Clin Med. 2022 Oct 8;11(19):5933. doi: 10.3390/jcm11195933. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36233800 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in health behavior and nutrient intake status between diabetes-aware and unaware Korean adults based on the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey 2016-18 data: A cross-sectional study.Front Public Health. 2022 Nov 3;10:1005369. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1005369. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36408042 Free PMC article.
-
Low relative hand grip strength is associated with a higher risk for diabetes and impaired fasting glucose among the Korean population.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 6;17(10):e0275746. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275746. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36201556 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between Bitter Taste Receptor Gene Variants and Dietary Intake Are Associated with the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Middle-Aged and Older Korean Adults.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 22;24(3):2199. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032199. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization: Global report on diabetes. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/204871 (cited 2020 Dec 18)
-
- World Health Organization: WHO Mortality Database. Available from: https://www.who.int/healthinfo/statistics/mort/en/ (cited 2020 Dec 18)
-
- Statistics Korea: Causes of death statistics in 2018. Available from: http://kostat.go.kr (cited 2020 Dec 18)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

