Cadherins, Selectins, and Integrins in CAM-DR in Leukemia
- PMID: 33425742
- PMCID: PMC7793796
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.592733
Cadherins, Selectins, and Integrins in CAM-DR in Leukemia
Abstract
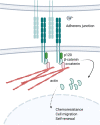
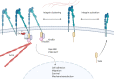
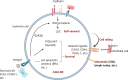
The interaction between leukemia cells and the bone microenvironment is known to provide drug resistance in leukemia cells. This phenomenon, called cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR), has been demonstrated in many subsets of leukemia including B- and T-acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B- and T-ALL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) are surface molecules that allow cell-cell or cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. CAMs not only recognize ligands for binding but also initiate the intracellular signaling pathways that are associated with cell proliferation, survival, and drug resistance upon binding to their ligands. Cadherins, selectins, and integrins are well-known cell adhesion molecules that allow binding to neighboring cells, ECM proteins, and soluble factors. The expression of cadherin, selectin, and integrin correlates with the increased drug resistance of leukemia cells. This paper will review the role of cadherins, selectins, and integrins in CAM-DR and the results of clinical trials targeting these molecules.
Keywords: bone marrow microenvironment; cell adhesion molecules; cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance; chemoresistance; leukemia.
Copyright © 2020 Kim, Ruan, Ogana and Kim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting integrins in drug-resistant acute myeloid leukaemia.Br J Pharmacol. 2024 Jan;181(2):295-316. doi: 10.1111/bph.16149. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Br J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37258706 Review.
-
Mechanisms of Cell Adhesion Molecules in Endocrine-Related Cancers: A Concise Outlook.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Apr 7;13:865436. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.865436. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35464064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Possible Importance of β3 Integrins for Leukemogenesis and Chemoresistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 15;19(1):251. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010251. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29342970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicle-cell adhesion molecules in tumours: biofunctions and clinical applications.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep 21;21(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01236-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37735659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of acute leukemia cells with the bone marrow microenvironment: implications for control of minimal residual disease.Leuk Lymphoma. 1995 Jun;18(1-2):1-16. doi: 10.3109/10428199509064917. Leuk Lymphoma. 1995. PMID: 8580810 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrins and the Metastasis-like Dissemination of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia to the Central Nervous System.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 27;15(9):2504. doi: 10.3390/cancers15092504. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37173970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pediatric Myeloid Sarcoma, More than Just a Chloroma: A Review of Clinical Presentations, Significance, and Biology.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 24;15(5):1443. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051443. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Automated workflow for the cell cycle analysis of (non-)adherent cells using a machine learning approach.Elife. 2024 Nov 22;13:RP94689. doi: 10.7554/eLife.94689. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39576677 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Faceted Effects of ST6Gal1 Expression on Precursor B-Lineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 16;12:828041. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.828041. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35371997 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of heat shock protein A12B (HSPA12B) in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Sep;9(18):1462. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-4185. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34734014 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gaynon PS, Qu RP, Chappell RJ, Willoughby ML, Tubergen DG, Steinherz PG, et al. Survival after relapse in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: impact of site and time to first relapse–the Children’s Cancer Group Experience. Cancer (1998) 82:1387–95. 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19980401)82:7<1387::AID-CNCR24>3.0.CO;2-1 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

