Pharmacological targeting of coagulation factor XI mitigates the development of experimental atherosclerosis in low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice
- PMID: 33421301
- PMCID: PMC8549080
- DOI: 10.1111/jth.15236
Pharmacological targeting of coagulation factor XI mitigates the development of experimental atherosclerosis in low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice
Abstract
Background: Human coagulation factor (F) XI deficiency, a defect of the contact activation system, protects against venous thrombosis, stroke, and heart attack, whereas FXII, plasma prekallikrein, or kininogen deficiencies are asymptomatic. FXI deficiency, inhibition of FXI production, activated FXI (FXIa) inhibitors, and antibodies to FXI that interfere with FXI/FXII interactions reduce experimental thrombosis and inflammation. FXI inhibitors are antithrombotic in patients, and FXI and FXII deficiencies are atheroprotective in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice.
Objectives: Investigate the effects of pharmacological targeting of FXI in experimental models of atherogenesis and established atherosclerosis.
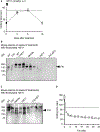
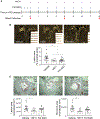
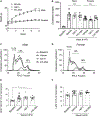
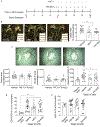
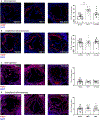
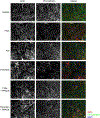
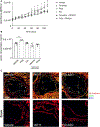
Methods and results: Low-density lipoprotein receptor-knockout (Ldlr-/- ) mice were administered high-fat diet (HFD) for 8 weeks; concomitantly, FXI was targeted with anti-FXI antibody (14E11) or FXI antisense oligonucleotide (ASO). 14E11 and FXI-ASO reduced atherosclerotic lesion area in proximal aortas when compared with controls, and 14E11 also reduced aortic sinus lesions. In an established disease model, in which therapy was given after atherosclerosis had developed, Ldlr-/- mice were fed HFD for 8 weeks and then administered 14E11 or FXI-ASO weekly until 16 weeks on HFD. In this established disease model, 14E11 and FXI-ASO reduced atherosclerotic lesion area in proximal aortas, but not in aortic sinus. In cultures of human endothelium, FXIa exposure disrupted VE-Cadherin expression and increased endothelial lipoprotein permeability. Strikingly, we found that 14E11 prevented the disruption of VE-Cadherin expression in aortic sinus lesions observed in the atherogenesis mouse model.
Conclusion: Pharmacological targeting of FXI reduced atherogenesis in Ldlr-/- mice. Interference with the contact activation system may safely reduce development or progression of atherosclerosis.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; contact activation; factor XI; obesity; vascular permeability.
© 2021 International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Dr. Revenko and Dr. Monia are employees of Ionis Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Gruber, Dr. Lorentz, Dr. Tucker, and the Oregon Health & Science University have a significant financial interest in Aronora, Inc., a company that may have a commercial interest in the results of this research. This potential conflict of interest has been reviewed and managed by the Oregon Health & Science University Conflict of Interest in Research Committee. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Factor XI Deficiency Protects Against Atherogenesis in Apolipoprotein E/Factor XI Double Knockout Mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Mar;36(3):475-81. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.306954. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26800563 Free PMC article.
-
A role for factor XIIa-mediated factor XI activation in thrombus formation in vivo.Blood. 2010 Nov 11;116(19):3981-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-02-270918. Epub 2010 Jul 15. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20634381 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological reduction of coagulation factor XI reduces macrophage accumulation and accelerates deep vein thrombosis resolution in a mouse model of venous thrombosis.J Thromb Haemost. 2022 Sep;20(9):2035-2045. doi: 10.1111/jth.15777. Epub 2022 Jul 18. J Thromb Haemost. 2022. PMID: 35638310 Free PMC article.
-
The hemostatic role of factor XI.Thromb Res. 2016 May;141 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S8-S11. doi: 10.1016/S0049-3848(16)30354-1. Thromb Res. 2016. PMID: 27207433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coagulation factor XI as a novel target for antithrombotic treatment.J Thromb Haemost. 2010 Nov;8(11):2349-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.04031.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2010. PMID: 20727068 Review.
Cited by
-
HK is the apple of FXI's eye.J Thromb Haemost. 2022 Nov;20(11):2485-2487. doi: 10.1111/jth.15842. J Thromb Haemost. 2022. PMID: 36271466 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Coming soon to a pharmacy near you? FXI and FXII inhibitors to prevent or treat thromboembolism.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2022 Dec 9;2022(1):495-505. doi: 10.1182/hematology.2022000386. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2022. PMID: 36485148 Free PMC article.
-
Factor XI as a therapeutic target in neuroinflammatory disease.Curr Opin Hematol. 2024 Jan 1;31(1):32-38. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000787. Epub 2023 Sep 5. Curr Opin Hematol. 2024. PMID: 37694771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferumoxytol-enhanced MRI assessment of venous Thrombus resolution and macrophage content in a murine deep vein thrombosis model.Thromb Res. 2024 Aug;240:109063. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2024.109063. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Thromb Res. 2024. PMID: 38878741
-
Removal of endothelial surface-associated von villebrand factor suppresses accelerate datherosclerosis after myocardial infarction.J Transl Med. 2024 May 1;22(1):412. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05231-6. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38693516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Libby P Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 2002;420:868–874. - PubMed
-
- Viles-Gonzalez JF, Fuster V, Badimon JJ. Atherothrombosis: a widespread disease with unpredictable and life-threatening consequences. Eur Heart J. 2004;25:1197–1207. - PubMed
-
- Leys D Atherothrombosis: a major health burden. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2001;11(Suppl. 2):1–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

