Use of hyaluronic acid injection after arthroscopic release in lateral patellar compression syndrome with degenerative cartilage changes: randomized control trial
- PMID: 33407337
- PMCID: PMC7786499
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-020-03876-0
Use of hyaluronic acid injection after arthroscopic release in lateral patellar compression syndrome with degenerative cartilage changes: randomized control trial
Abstract
Background: Degenerative cartilage changes can be seen, in cases of lateral patellar compression syndrome, involving the patellofemoral joint. Hyaluronic acid is a natural component of the synovial fluid and responsible for its elastic features and function of articular surfaces. The aim of this study is to show the effect of intra-articular injection of Hyaluronic acid, after arthroscopic lateral release in lateral patellar compression syndrome, on the functional outcome and knee pain in those patients with degenerative cartilage changes.
Method: Ninety patients age (30-50) years with lateral patellar compression syndrome and degenerative cartilage changes were divided randomly into 2 groups. Group A was treated by arthroscopic lateral release and received intraarticular injection of Hyaluronic acid 2 weeks after surgery. Group B was treated by arthroscopic lateral release only. Both groups were assessed by Kujala score and visual analogue scale for knee pain preoperatively and re-assessed postoperatively at 3 months, 6 months, 12 months and 24 months.
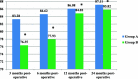
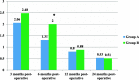
Results: There was significant improvement in Kujala score and Visual analogue scale post-operatively in both groups (P-value< 0.001) with better improvement in Kujala score in group A after intra-articular injection of Hyaluronic acid up to 2 year of follow up (P-value = 0.006) as well as better improvement in visual analogue score at 6 months post-operatively (P-value = 0.035).
Conclusion: Intra-articular injection of Hyaluronic acid after arthroscopic release, in patients with lateral patellar compression syndrome and degenerative cartilage changes, can result in better improvement of knee pain and functional outcome up to 2 years of follow up.
Trial registration: NCT, NCT04134611 . Registered 18 October 2019 -Retrospectively registered.
Keywords: Arthroscopic release; Functional outcome; Hyaluronic acid injection; Knee pain; Kujala score; Lateral patellar compression syndrome; Visual analogue scale.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declare that he has no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and experience of arthroscopic lateral patella retinaculum releasing through/outside synovial membrane for the treatment of lateral patellar compression syndrome.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020 Feb 17;21(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-3130-y. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020. PMID: 32066436 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Open versus arthroscopic release for lateral patellar compression syndrome: a randomized-controlled trial.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022 Oct;142(10):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s00402-021-03878-0. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022. PMID: 33829300 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Proposal of a therapeutic protocol for selected patients with patellofemoral knee osteoarthritis: arthroscopic lateral retinacular release followed by viscosupplementation.Musculoskelet Surg. 2016 Dec;100(3):171-178. doi: 10.1007/s12306-016-0402-7. Epub 2016 Mar 26. Musculoskelet Surg. 2016. PMID: 27017345
-
Intra-articular injection of autologous adipose-derived stromal vascular fractions for knee osteoarthritis: a double-blind randomized self-controlled trial.Int Orthop. 2019 May;43(5):1123-1134. doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-4099-0. Epub 2018 Aug 14. Int Orthop. 2019. PMID: 30109404 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of Fabella syndrome with arthroscopic fabellectomy: a case series and literature review.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Aug 30;22(1):748. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04630-w. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021. PMID: 34461874 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ficat P, Ficat C, Bailleux A. Syndrome d'hyperpression externe de la rotule (S.H.P.E.). son intérêt pour la connaissance de l'arthrose [external hypertension syndrome of the patella. Its significance in the recognition of arthrosis] Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1975;61(1):39–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources