COVID-19 epidemic in Libya
- PMID: 33407008
- PMCID: PMC7801096
- DOI: 10.1080/19932820.2021.1871798
COVID-19 epidemic in Libya
Abstract
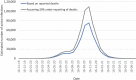
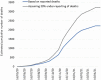
The first case of COVID-19 was identified in Libya on 24/3/2020, and about 2 months later, the number of reported COVID-19 cases started to increase notably. The outbreak was first prominent in the southern region (Sabha) and then spread to the western and eastern parts of Libya. By 24/12/2020, the reported total number of deaths from COVID-19 reached 1415. There seems to be no published data on the size of the epidemic in Libya. Here, we estimated the number of Libyans exposed to COVID-19 by using a COVID-19 mortality adjusted mathematical model for the spread of infectious diseases. We estimated that 14-20% of the Libyan population have been exposed to the COVID-19 pandemic. Thus, the risk of spread of COVID-19 infections during the coming months is high, and a considerable number of Libyans, particularly the elderly and people with chronic diseases, should be protected against COVID-19 infection. This is particularly urgent in the light of unofficial reports that the relevant healthcare facilities are under extreme stress.
Keywords: COVID-19; Libya; epidemic spread; modeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Epidemiological and Spatiotemporal Characteristics of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) in Libya.Front Public Health. 2021 Jun 14;9:628211. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.628211. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34195168 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Armed Conflict on the Epidemiological Situation of COVID-19 in Libya, Syria and Yemen.Front Public Health. 2021 Jun 11;9:667364. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.667364. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34178925 Free PMC article.
-
The epidemiological characteristics of COVID-19 in Libya during the ongoing-armed conflict.Pan Afr Med J. 2020 Nov 5;37:219. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2020.37.219.24993. eCollection 2020. Pan Afr Med J. 2020. PMID: 33520058 Free PMC article.
-
How do surgeons weather the storm of COVID-19 pandemic?Med J Malaysia. 2020 Nov;75(6):762-763. Med J Malaysia. 2020. PMID: 33219197 Review.
-
Battling COVID-19 pandemic waves in six South-East Asian countries: A real-time consensus review.Med J Malaysia. 2020 Nov;75(6):613-625. Med J Malaysia. 2020. PMID: 33219168 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence and associated factors of COVID-19 among Moroccan physicians: A cross-sectional study.PLoS One. 2022 Nov 2;17(11):e0277157. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277157. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36322588 Free PMC article.
-
Hospitalization among vaccines for SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infection after dose sparing strategies in Libya: A cohort study.PLoS One. 2022 Nov 3;17(11):e0276425. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276425. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36327290 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the Mediterranean region over 18 months: bridging the health outcomes and sustainable development goals.Afr Health Sci. 2022 Dec;22(4):551-564. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v22i4.61. Afr Health Sci. 2022. PMID: 37113533 Free PMC article.
-
Infectious disease modelling for SARS-CoV-2 in Africa to guide policy: A systematic review.Epidemics. 2022 Sep;40:100610. doi: 10.1016/j.epidem.2022.100610. Epub 2022 Jul 14. Epidemics. 2022. PMID: 35868211 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WorldBank . Population profile of Libya. World Bank Group, Washington DC; 2020. Available from https://data.worldbank.org/country/libya
-
- ECDC . Epidemiology of COVID-19. European centre for disease prevention and control; 2020; Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/covid-19/latest-evidence.
-
- Folkhälsomyndigheten . The infection fatality rate of COVID-19 in Stockholm – technical report, article 2009, 4-2. Public Health Agency of Sweden, Solna, Sweden; 2020. Available from https://www.folkhalsomyndigheten.se/publicerat-material/publikationsarki...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical