From genes polymorphisms to mucosal expression of cytokines: evaluating IL-23/IL-17 axis in adult patients with gastritis
- PMID: 33402994
- PMCID: PMC7751554
- DOI: 10.4314/ahs.v20i3.51
From genes polymorphisms to mucosal expression of cytokines: evaluating IL-23/IL-17 axis in adult patients with gastritis
Abstract
Background and objective: Chronic inflammation is the typical sign of gastritis that may shift into gastric cancer. IL-17A and IL-17F as a novel inflammatory cytokines subset of CD4+Th play the main role in inflammation. A key cytokine receptor in the inflammatory IL-17/IL-23 axis, the interleukin 23 receptor (IL23R), may be related to gastritis. We evaluated the correspondence between IL-17A G197A, IL-17F A7488G and IL23R+2199 A/C polymorphisms with TGF-β1, IL-6, IL-17, IL-21 and IL-23 mucosal mRNAs expression in uninfected H. Pylori (HP) chronic gastritis patients.
Materials and methods: Total RNA and genomic DNA were separated from gastric biopsies of 44 patients with gastritis. Subsequently, mucosal mRNAs expression of TGF-β1, IL-6, IL-17, IL-21 and IL-23 were assessed by real-time PCR. To polymorphisms determination of IL-17A G197A, IL-17F A7488G and IL-23R +2199A/C the PCR-RFLP was used in gastric biopsies.
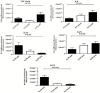
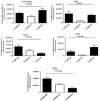
Results: Results point that IL-17A G197A, IL-17F A7488G and IL23R +2199A/C polymorphisms did not influence the mucosal expression of TGF-β1, IL-6, IL-17 and IL-21 (p> 0.05). In an opposite result, we don't find a correspondence between IL-17A G197A, IL-17F A7488G polymorphisms and mucosal expression of IL-23 (p> 0.05). In a contrary, we found a correlation between IL23R +2199A/C polymorphism and mucosal expression of IL-23 in patients with chronic gastritis (p< 0.05).
Conclusion: These findings propose that IL23R +2199A/C polymorphism may change the mucosal expression of IL-23 pattern in patients with gastritis disease in the absence of HP, but to support the conclusion, more research may be required.
Keywords: Cytokines; IL-23, IL-17; gastritis; polymorphism.
© 2020 Azadegan-Dehkordi F et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
New insight to IL-23/IL-17 axis in Iranian infected adult patients with gastritis: effects of genes polymorphisms on expression of cytokines.Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2015 Jun;78(2):212-8. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2015. PMID: 26151690
-
Cytokine gene polymorphisms influence mucosal cytokine expression, gastric inflammation, and host specific colonisation during Helicobacter pylori infection.Gut. 2004 Aug;53(8):1082-9. doi: 10.1136/gut.2003.029736. Gut. 2004. PMID: 15247172 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent Helicobacter pylori specific Th17 responses in patients with past H. pylori infection are associated with elevated gastric mucosal IL-1β.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39199. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039199. Epub 2012 Jun 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22761739 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of inflammatory cytokine polymorphisms on eradication rates of Helicobacter pylori.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009 Nov;24(11):1725-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.06047.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 20136959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Roles of IL-17, IL-21, and IL-23 in the Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastrointestinal Inflammation: A Review.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Apr 28;13(5):315. doi: 10.3390/toxins13050315. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33924897 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin- 17agene Polymorphism, Serum Level and Its Tissue Expression in Iraqi Patients Gastric Lesions.Med Arch. 2021 Feb;75(1):23-26. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2021.75.23-26. Med Arch. 2021. PMID: 34012194 Free PMC article.
-
Twenty years of African Health Sciences as infections continue to plague our continent.Afr Health Sci. 2020 Sep;20(3):i-vi. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v20i3.1. Afr Health Sci. 2020. PMID: 33403000 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ahmadi A, Zandi F, Gharib A, Menbari N, Hosseini J, Abdi M, et al. Relationship Between Polymorphism in Promoter Region of E-Cadherin (Cdh1) Gene and Helicobacter Pylori Infection in Kurdish Population of Iran. Life Science Journal. 2013;10(12s)
-
- Salimzadeh L, Bagheri N, Zamanzad B, Azadegan-Dehkordi F, Rahimian G, Hashemzadeh-Chaleshtori M, et al. Frequency of virulence factors in Helicobacter pylori-infected patients with gastritis. Microb Pathog. 2015;80:67–72. PubMed. - PubMed
-
- Menbari MN, Rahmani SA, Ahmadi A, Zandi F, Bagheri N, Jalili A, et al. Evaluation of E-cadherin (CDH1) Gene Polymorphism Related To Gastric Cancer In Kurdish Population. Life Science Journal. 2013;10(12s)
-
- Bagheri N, Azadegan-Dehkordi F, Sanei H, Taghikhani A, Rahimian G, Salimzadeh L, et al. Associations of a TLR4 single-nucleotide polymorphism with H. pylori associated gastric diseases in Iranian patients. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2014;38(3):366–371. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
