Type IA Topoisomerases as Targets for Infectious Disease Treatments
- PMID: 33401386
- PMCID: PMC7823277
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9010086
Type IA Topoisomerases as Targets for Infectious Disease Treatments
Abstract
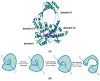
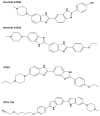
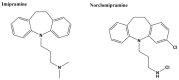
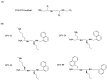
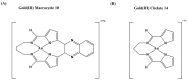
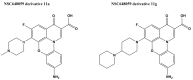
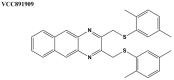
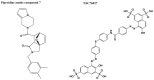
Infectious diseases are one of the main causes of death all over the world, with antimicrobial resistance presenting a great challenge. New antibiotics need to be developed to provide therapeutic treatment options, requiring novel drug targets to be identified and pursued. DNA topoisomerases control the topology of DNA via DNA cleavage-rejoining coupled to DNA strand passage. The change in DNA topological features must be controlled in vital processes including DNA replication, transcription, and DNA repair. Type IIA topoisomerases are well established targets for antibiotics. In this review, type IA topoisomerases in bacteria are discussed as potential targets for new antibiotics. In certain bacterial pathogens, topoisomerase I is the only type IA topoisomerase present, which makes it a valuable antibiotic target. This review will summarize recent attempts that have been made to identify inhibitors of bacterial topoisomerase I as potential leads for antibiotics and use of these inhibitors as molecular probes in cellular studies. Crystal structures of inhibitor-enzyme complexes and more in-depth knowledge of their mechanisms of actions will help to establish the structure-activity relationship of potential drug leads and develop potent and selective therapeutics that can aid in combating the drug resistant bacterial infections that threaten public health.
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance; drug targets; topoisomerase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring DNA topoisomerases as targets of novel therapeutic agents in the treatment of infectious diseases.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2007 Mar;7(1):3-9. doi: 10.2174/187152607780090748. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2007. PMID: 17346206 Review.
-
What's on the Other Side of the Gate: A Structural Perspective on DNA Gate Opening of Type IA and IIA DNA Topoisomerases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 16;24(4):3986. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043986. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Variation of Structure and Cellular Functions of Type IA Topoisomerases across the Tree of Life.Cells. 2024 Mar 21;13(6):553. doi: 10.3390/cells13060553. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38534397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA Topoisomerases as Targets for Antibacterial Agents.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1703:47-62. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7459-7_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29177732
-
Inhibition of Zn(II) binding type IA topoisomerases by organomercury compounds and Hg(II).PLoS One. 2015 Mar 23;10(3):e0120022. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120022. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25798600 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Success stories of natural product-derived compounds from plants as multidrug resistance modulators in microorganisms.RSC Adv. 2023 Mar 8;13(12):7798-7817. doi: 10.1039/d3ra00184a. eCollection 2023 Mar 8. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 36909750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of a pathway of genomic instability induced by R-loops and its regulation by topoisomerases in E. coli.PLoS Genet. 2023 May 4;19(5):e1010754. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010754. eCollection 2023 May. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37141391 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the DNA and RNA Interactions of Human Topoisomerase III Beta Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations.J Chem Inf Model. 2024 Aug 12;64(15):6062-6071. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.4c00472. Epub 2024 Jul 18. J Chem Inf Model. 2024. PMID: 39024468 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

