Cytosolic Ca2+ transients during pulsed focused ultrasound generate reactive oxygen species and cause DNA damage in tumor cells
- PMID: 33391495
- PMCID: PMC7738866
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.48353
Cytosolic Ca2+ transients during pulsed focused ultrasound generate reactive oxygen species and cause DNA damage in tumor cells
Abstract
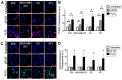
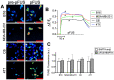
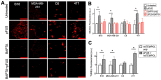
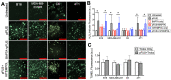
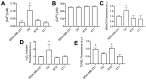
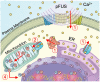
Mechanical forces from non-ablative pulsed focused ultrasound (pFUS) generate pro-inflammatory tumor microenvironments (TME), marked by increased cytokines, chemokines, and trophic factors, as well as immune cell infiltration and reduced tumor growth. pFUS also causes DNA damage within tumors, which is a potent activator of immunity and could contribute to changes in the TME. This study investigated mechanisms behind the mechanotransductive effects of pFUS causing DNA damage in several tumor cell types. Methods: 4T1 (murine breast tumor), B16 (murine melanoma), C6 (rat glioma), or MDA-MB-231 (human breast tumor) cells were sonicated in vitro (1.1MHz; 6MPa PNP; 10ms pulses; 10% duty cycle; 300 pulses). DNA damage was detected by TUNEL, apoptosis was measured by immunocytochemistry for cleaved caspase-3. Calcium, superoxide, and H2O2 were detected by fluorescent indicators and modulated by BAPTA-AM, mtTEMPOL, or Trolox, respectively. Results: pFUS increased TUNEL reactivity (range = 1.6-2.7-fold) in all cell types except C6 and did not induce apoptosis in any cell line. All lines displayed cytosolic Ca2+ transients during sonication. pFUS increased superoxide (range = 1.6-2.0-fold) and H2O2 (range = 2.3-2.8-fold) in all cell types except C6. BAPTA-AM blocked increased TUNEL reactivity, superoxide and H2O2 formation, while Trolox also blocked increased TUNEL reactivity increased after pFUS. mtTEMPOL allowed H2O2 formation and did not block increased TUNEL reactivity after pFUS. Unsonicated C6 cells had higher baseline concentrations of cytosolic Ca2+, superoxide, and H2O2, which were not associated with greater baseline TUNEL reactivity than the other cell lines. Conclusions: Mechanotransduction of pFUS directly induces DNA damage in tumor cells by cytosolic Ca2+ transients causing formation of superoxide and subsequently, H2O2. These results further suggest potential clinical utility for pFUS. However, the lack of pFUS-induced DNA damage in C6 cells demonstrates a range of potential tumor responses that may arise from physiological differences such as Ca2+ or redox homeostasis.
Keywords: DNA damage; calcium; focused ultrasound; reactive oxygen species; tumor.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pulsed-Focused Ultrasound Slows B16 Melanoma and 4T1 Breast Tumor Growth through Differential Tumor Microenvironmental Changes.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 27;13(7):1546. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071546. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33801627 Free PMC article.
-
The Proteomic Effects of Pulsed Focused Ultrasound on Tumor Microenvironments of Murine Melanoma and Breast Cancer Models.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019 Dec;45(12):3232-3245. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2019.08.014. Epub 2019 Sep 14. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31530419 Free PMC article.
-
Focused ultrasound activates voltage-gated calcium channels through depolarizing TRPC1 sodium currents in kidney and skeletal muscle.Theranostics. 2019 Jul 28;9(19):5517-5531. doi: 10.7150/thno.33876. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31534500 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium signaling in cancer and vitamin D.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2005 Oct;97(1-2):145-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2005.06.007. Epub 2005 Aug 2. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16081284 Review.
-
Peripheral focused ultrasound stimulation and its applications: From therapeutics to human-computer interaction.Front Neurosci. 2023 Apr 14;17:1115946. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1115946. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37123351 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Latest Advances in the Use of Therapeutic Focused Ultrasound in the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 27;14(3):638. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030638. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35158903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulsed-Focused Ultrasound Slows B16 Melanoma and 4T1 Breast Tumor Growth through Differential Tumor Microenvironmental Changes.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 27;13(7):1546. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071546. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33801627 Free PMC article.
-
The role of APTX4870 peptide in reducing cellular inflammatory responses by inhibiting Mycobacterium tuberculosis-derived mycolic acid-induced cytotoxicity.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 24;13:993897. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.993897. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36353454 Free PMC article.
-
Application of calcium overload-based ion interference therapy in tumor treatment: strategies, outcomes, and prospects.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 15;15:1352377. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1352377. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38425645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Permeation Challenges of Drugs for Treatment of Neurological Tuberculosis and HIV and the Application of Magneto-Electric Nanoparticle Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Sep 15;13(9):1479. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091479. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34575555 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Elhelf IAS, Albahar H, Shah U, Oto A, Cressman E, Almekkawy M. High intensity focused ultrasound: The fundamentals, clinical applications and research trends. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2018;99:349–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

