S100A8 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis under TGF-β/USF2 axis in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 33389821
- PMCID: PMC7896751
- DOI: 10.1002/cac2.12130
S100A8 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis under TGF-β/USF2 axis in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: The transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) pathway plays a pivotal role in inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which is a key step in cancer invasion and metastasis. However, the regulatory mechanism of TGF-β in inducing EMT in colorectal cancer (CRC) has not been fully elucidated. In previous studies, it was found that S100A8 may regulate EMT. This study aimed to clarify the role of S100A8 in TGF-β-induced EMT and explore the underlying mechanism in CRC.
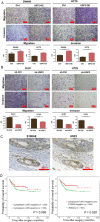
Methods: S100A8 and upstream transcription factor 2 (USF2) expression was detected by immunohistochemistry in 412 CRC tissues. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was performed. In vitro, Western blot, and migration and invasion assays were performed to investigate the effects of S100A8 and USF2 on TGF-β-induced EMT. Mouse metastasis models were used to determine in vivo metastasis ability. Luciferase reporter and chromatin immunoprecipitation assay were used to explore the role of USF2 on S100A8 transcription.
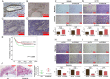
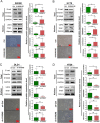
Results: During TGF-β-induced EMT in CRC cells, S100A8 and the transcription factor USF2 were upregulated. S100A8 promoted cell migration and invasion and EMT. USF2 transcriptionally regulated S100A8 expression by directly binding to its promoter region. Furthermore, TGF-β enhanced the USF2/S100A8 signaling axis of CRC cells whereas extracellular S100A8 inhibited the USF2/S100A8 axis of CRC cells. S100A8 expression in tumor cells was associated with poor overall survival in CRC. USF2 expression was positively related to S100A8 expression in tumor cells but negatively related to S100A8-positive stromal cells.
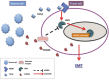
Conclusions: TGF-β was found to promote EMT and metastasis through the USF2/S100A8 axis in CRC while extracellular S100A8 suppressed the USF2/S100A8 axis. USF2 was identified as an important switch on the intracellular and extracellular S100A8 feedback loop.
Keywords: S100 calcium-binding protein A8; colorectal cancer; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; metastasis; prognosis; transforming growth factor-β; upstream transcription factor 2.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Communications published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd. on behalf of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Resveratrol suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer through TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway mediated Snail/E-cadherin expression.BMC Cancer. 2015 Mar 5;15:97. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1119-y. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25884904 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA SNHG6 promotes proliferation, invasion and migration in colorectal cancer cells by activating TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway via targeting UPF1 and inducing EMT via regulation of ZEB1.Int J Med Sci. 2019 Jan 1;16(1):51-59. doi: 10.7150/ijms.27359. eCollection 2019. Int J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30662328 Free PMC article.
-
NR2F2 inhibits Smad7 expression and promotes TGF-β-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition of CRC via transactivation of miR-21.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Mar 25;485(1):181-188. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.02.049. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28192117
-
Role of Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 1;24(19):14815. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914815. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the function of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in colorectal cancer: Metastasis, therapy response, and revisiting molecular pathways.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Apr;160:114395. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114395. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36804124 Review.
Cited by
-
(S)-10-Hydroxycamptothecin Inhibits EMT-evoked Osteosarcoma Cell Growth and Metastasis by Activating the HIPPO Signaling Pathway.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(15):2239-2248. doi: 10.2174/0113862073263020231220043405. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 38369725
-
Cytokine- and chemokine-induced inflammatory colorectal tumor microenvironment: Emerging avenue for targeted therapy.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2022 Aug;42(8):689-715. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12295. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35791509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell and spatial transcriptome analyses revealed cell heterogeneity and immune environment alternations in metastatic axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023 Mar;72(3):679-695. doi: 10.1007/s00262-022-03278-2. Epub 2022 Aug 30. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023. PMID: 36040519 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of research progress and application of experimental models of colorectal cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 4;14:1193213. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1193213. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37469864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HRC promotes anoikis resistance and metastasis by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Jun 26;18(14):3112-3124. doi: 10.7150/ijms.60610. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34400882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(1):7‐30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

