Physcion Protects Against Ethanol-Induced Liver Injury by Reprogramming of Circadian Clock
- PMID: 33381029
- PMCID: PMC7768821
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.573074
Physcion Protects Against Ethanol-Induced Liver Injury by Reprogramming of Circadian Clock
Abstract
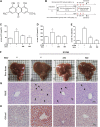
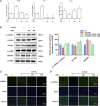
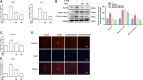
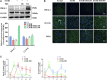
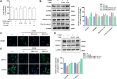
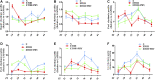
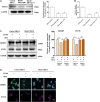
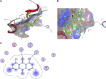
The circadian clock plays a key role in our daily physiology and metabolism. Alcohol consumption disrupts the circadian rhythm of metabolic genes in the liver; however, the potential contribution of circadian clock modulation to alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is unknown. We identified a novel liver protective agent, physcion, which can alleviate fat accumulation and inflammation in ALD mice via reprogramming the hepatic circadian clock. The model of alcoholic hepatitis was established by intragastrically administering ethanol. In vitro, physcion was investigated by treating HepG2 cells with ethanol. The role of circadian clock in Physcion caused liver protection was tested by knocking down the core circadian gene Bmal1. Physcion application caused reduced lipogenesis and alleviated inflammation in alcohol-induced mice. In alcoholic hepatosteatosis models, physcion upregulated the core circadian genes. And the circadian misalignment triggered by ethanol was efficiently reversed by physcion. Physcion attenuated lipogenesis via reprogramming the circadian clock in HepG2 cells. Suppression of Bmal1 by RNA interference abolished the protective of physcion. In addition, Physcion binds to the active pocket of BMAL1 and promotes its expression. The study identified the novel liver protective effects of physcion on alcohol-induced liver injury, and modulation of the core circadian clock regulators contributes to ALD alleviation. More importantly, strategies targeting the circadian machinery, for example, Bmal1, may prove to be beneficial treatment options for this condition.
Keywords: alcoholic liver steatosis; circadian clock; inflammation; lipogenesis; physcion.
Copyright © 2020 Yao, Zuo, Deng, Liu, Zhan, Wang, Xu, Ma, and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The hepatic BMAL1/AKT/lipogenesis axis protects against alcoholic liver disease in mice via promoting PPARα pathway.Hepatology. 2018 Sep;68(3):883-896. doi: 10.1002/hep.29878. Epub 2018 May 20. Hepatology. 2018. PMID: 29534306 Free PMC article.
-
Nobiletin Protects Against Alcoholic Liver Disease in Mice via the BMAL1-AKT-Lipogenesis Pathway.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2024 Jun;68(12):e2300833. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202300833. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2024. PMID: 38850176
-
Deletion of circadian gene Per1 alleviates acute ethanol-induced hepatotoxicity in mice.Toxicology. 2013 Dec 15;314(2-3):193-201. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2013.09.009. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Toxicology. 2013. PMID: 24144995
-
Emerging role of circadian clock disruption in alcohol-induced liver disease.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018 Sep 1;315(3):G364-G373. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00010.2018. Epub 2018 May 31. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29848023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circadian rhythms, alcohol and gut interactions.Alcohol. 2015 Jun;49(4):389-98. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2014.07.021. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Alcohol. 2015. PMID: 25499101 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Effects of Melatonin in the Regulation of Ferroptosis: A Review of Current Evidence.Curr Drug Targets. 2024;25(8):543-557. doi: 10.2174/0113894501284110240426074746. Curr Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38706348 Review.
-
Quality assessment of Rheum species cultivated in Japan by focusing on M2 polarization of microglia.J Nat Med. 2023 Sep;77(4):699-711. doi: 10.1007/s11418-023-01710-0. Epub 2023 Jun 22. J Nat Med. 2023. PMID: 37347410
-
Network pharmacology analysis and molecular docking to unveil the potential mechanisms of San-Huang-Chai-Zhu formula treating cholestasis.PLoS One. 2022 Feb 23;17(2):e0264398. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264398. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35196362 Free PMC article.
-
Physcion inhibition of CYP2C9, 2D6 and 3A4 in human liver microsomes.Pharm Biol. 2024 Dec;62(1):207-213. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2024.2314089. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Pharm Biol. 2024. PMID: 38353248 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Anthraquinones on Immune Responses and Inflammatory Diseases.Molecules. 2022 Jun 14;27(12):3831. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123831. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35744949 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clementi E. M., Misiti F. (2010). Potential health benefits of rhubarb. Bioact. Foods Promot. Health, 407–423. 10.1016/B978-0-12-374628-3.00027-X - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

