Simultaneous Quantification of Antioxidants Paraxanthine and Caffeine in Human Saliva by Electrochemical Sensing for CYP1A2 Phenotyping
- PMID: 33374269
- PMCID: PMC7823619
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10010010
Simultaneous Quantification of Antioxidants Paraxanthine and Caffeine in Human Saliva by Electrochemical Sensing for CYP1A2 Phenotyping
Abstract
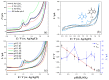
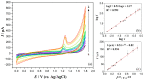
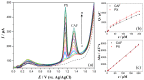
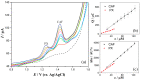
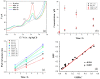
The enzyme CYP1A2 is responsible for the metabolism of numerous antioxidants in the body, including caffeine, which is transformed into paraxanthine, its main primary metabolite. Both molecules are known for their antioxidant and pro-oxidant characteristics, and the paraxanthine-to-caffeine molar ratio is a widely accepted metric for CYP1A2 phenotyping, to optimize dose-response effects in individual patients. We developed a simple, cheap and fast electrochemical based method for the simultaneous quantification of paraxanthine and caffeine in human saliva, by differential pulse voltammetry, using an anodically pretreated glassy carbon electrode. Cyclic voltammetry experiments revealed for the first time that the oxidation of paraxanthine is diffusion controlled with an irreversible peak at ca. +1.24 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) in a 0.1 M H2SO4 solution, and that the mechanism occurs via the transfer of two electrons and two protons. The simultaneous quantification of paraxanthine and caffeine was demonstrated in 0.1 M H2SO4 and spiked human saliva samples. In the latter case, limits of detection of 2.89 μM for paraxanthine and 5.80 μM for caffeine were obtained, respectively. The sensor is reliable, providing a relative standard deviation within 7% (n = 6). Potential applicability of the sensing platform was demonstrated by running a small scale trial on five healthy volunteers, with simultaneous quantification by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) of paraxanthine and caffeine in saliva samples collected at 1, 3 and 6 h postdose administration. The results were validated by ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography and shown to have a high correlation factor (r = 0.994).
Keywords: CYP1A2 phenotyping; antioxidants; caffeine; differential pulse voltammetry; human saliva; paraxanthine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
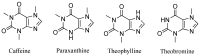
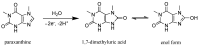
Similar articles
-
Simple and reliable CYP1A2 phenotyping by the paraxanthine/caffeine ratio in plasma and in saliva.Pharmacogenetics. 1994 Jun;4(3):109-16. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199406000-00001. Pharmacogenetics. 1994. PMID: 7920690 Clinical Trial.
-
Development and validation of a reversed-phase HPLC method for CYP1A2 phenotyping by use of a caffeine metabolite ratio in saliva.Biomed Chromatogr. 2015 Nov;29(11):1657-63. doi: 10.1002/bmc.3475. Epub 2015 Apr 19. Biomed Chromatogr. 2015. PMID: 25891161
-
Analysis of caffeine and paraxanthine in human saliva with ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography for CYP1A2 phenotyping.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015 Jul 15;995-996:70-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.05.020. Epub 2015 May 18. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26038236
-
Assessment of CYP1A2 activity in clinical practice: why, how, and when?Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005 Sep;97(3):125-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2005.pto_973160.x. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005. PMID: 16128905 Review.
-
Caffeine metabolic ratios for the in vivo evaluation of CYP1A2, N-acetyltransferase 2, xanthine oxidase and CYP2A6 enzymatic activities.Curr Drug Metab. 2009 May;10(4):329-38. doi: 10.2174/138920009788499003. Curr Drug Metab. 2009. PMID: 19519341 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactive compounds in coffee and their role in lowering the risk of major public health consequences: A review.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Nov 22;12(2):734-764. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3848. eCollection 2024 Feb. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38370073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein-Nanoparticle Interactions Govern the Interfacial Behavior of Polymeric Nanogels: Study of Protein Corona Formation at the Air/Water Interface.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 1;24(3):2810. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032810. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769129 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensors for Caffeine Determination.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 25;22(23):9185. doi: 10.3390/s22239185. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36501886 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

