Cancer-Induced Muscle Wasting Requires p38β MAPK Activation of p300
- PMID: 33355181
- PMCID: PMC8456613
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-3219
Cancer-Induced Muscle Wasting Requires p38β MAPK Activation of p300
Abstract
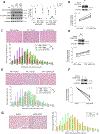
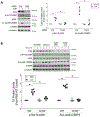
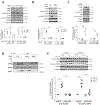
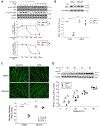
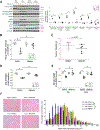
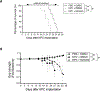
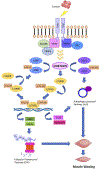
Cancer-associated cachexia, characterized by muscle wasting, is a lethal metabolic syndrome without defined etiology or established treatment. We previously found that p300 mediates cancer-induced muscle wasting by activating C/EBPβ, which then upregulates key catabolic genes. However, the signaling mechanism that activates p300 in response to cancer is unknown. Here, we show that upon cancer-induced activation of Toll-like receptor 4 in skeletal muscle, p38β MAPK phosphorylates Ser-12 on p300 to stimulate C/EBPβ acetylation, which is necessary and sufficient to cause muscle wasting. Thus, p38β MAPK is a central mediator and therapeutic target of cancer-induced muscle wasting. In addition, nilotinib, an FDA-approved kinase inhibitor that preferentially binds p38β MAPK, inhibited p300 activation 20-fold more potently than the p38α/β MAPK inhibitor, SB202190, and abrogated cancer cell-induced muscle protein loss in C2C12 myotubes without suppressing p38α MAPK-dependent myogenesis. Systemic administration of nilotinib at a low dose (0.5 mg/kg/day, i.p.) in tumor-bearing mice not only alleviated muscle wasting, but also prolonged survival. Therefore, nilotinib appears to be a promising treatment for human cancer cachexia due to its selective inhibition of p38β MAPK. SIGNIFICANCE: These findings demonstrate that prevention of p38β MAPK-mediated activation of p300 by the FDA-approved kinase inhibitor, nilotinib, ameliorates cancer cachexia, representing a potential therapeutic strategy against this syndrome.
©2020 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
C/EBPβ mediates tumour-induced ubiquitin ligase atrogin1/MAFbx upregulation and muscle wasting.EMBO J. 2011 Aug 16;30(20):4323-35. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.292. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21847090 Free PMC article.
-
Valproic acid attenuates skeletal muscle wasting by inhibiting C/EBPβ-regulated atrogin1 expression in cancer cachexia.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016 Jul 1;311(1):C101-15. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00344.2015. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27122162
-
Signaling mechanism of tumor cell-induced up-regulation of E3 ubiquitin ligase UBR2.FASEB J. 2013 Jul;27(7):2893-901. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-222711. Epub 2013 Apr 8. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23568773 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways of angiotensin II-induced muscle wasting: potential therapeutic targets for cardiac cachexia.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Oct;45(10):2322-32. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.05.035. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23769949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Muscle wasting in cancer.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Oct;45(10):2215-29. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.05.032. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23770121 Review.
Cited by
-
UBR2 targets myosin heavy chain IIb and IIx for degradation: Molecular mechanism essential for cancer-induced muscle wasting.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Oct 25;119(43):e2200215119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2200215119. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36252004 Free PMC article.
-
Corylifol A ameliorates muscle atrophy by inhibiting TAOK1/p38-MAPK/FoxO3 pathway in cancer cachexia.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023 Oct;14(5):2098-2113. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13288. Epub 2023 Jul 13. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023. PMID: 37439183 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Regulation of Tceal7 by the Triple Complex of Mef2c, Creb1 and Myod.Biology (Basel). 2022 Mar 16;11(3):446. doi: 10.3390/biology11030446. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35336819 Free PMC article.
-
Weight Loss in Cancer Patients Correlates With p38β MAPK Activation in Skeletal Muscle.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Dec 7;9:784424. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.784424. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34950660 Free PMC article.
-
The epigenetic regulatory effect of histone acetylation and deacetylation on skeletal muscle metabolism-a review.Front Physiol. 2023 Dec 8;14:1267456. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1267456. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 38148899 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fearon KC, Glass DJ, Guttridge DC. Cancer cachexia: mediators, signaling, and metabolic pathways. Cell metabolism 2012;16:153–66 - PubMed
-
- Fearon K, Strasser F, Anker SD, Bosaeus I, Bruera E, Fainsinger RL, et al.Definition and classification of cancer cachexia: an international consensus. Lancet Oncol 2011;12:489–95 - PubMed
-
- Andreyev HJ, Norman AR, Oates J, Cunningham D. Why do patients with weight loss have a worse outcome when undergoing chemotherapy for gastrointestinal malignancies? Eur J Cancer 1998;34:503–9 - PubMed
-
- Baracos VE, Martin L, Korc M, Guttridge DC, Fearon KCH. Cancer-associated cachexia. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2018;4:17105 - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 2020;70:7–30 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

