The unique features of SARS-CoV-2 transmission: Comparison with SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and 2009 H1N1 pandemic influenza virus
- PMID: 33350025
- PMCID: PMC7537046
- DOI: 10.1002/rmv.2171
The unique features of SARS-CoV-2 transmission: Comparison with SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and 2009 H1N1 pandemic influenza virus
Abstract
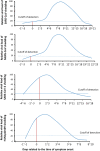
From 2002 to 2019, three deadly human coronaviruses (hCoVs), severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), Middle Eastern respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) emerged to produce outbreaks of SARS, MERS and coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19), respectively. All three hCoVs are members of the Betacoronavirus genus in the subfamily Orthocoronavirinae and share many similarities in virology and epidemiology. However, the pattern and scale of Covid-19 global spread is similar to 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza (H1N1pdm09), rather than SARS or MERS. Covid-19 exhibits high viral shedding in the upper respiratory tract at an early stage of infection, and has a high proportion of transmission competent individuals that are pre-symptomatic, asymptomatic and mildly symptomatic, characteristics seen in H1N1pdm09 but not in SARS or MERS. These two traits of Covid-19 and H1N1pdm09 result in reduced efficiency in identification of transmission sources by symptomatic screening and play important roles in their ability to spread unchecked to cause pandemics. To overcome these attributes of Covid-19 in community transmission, identifying the transmission source by testing for virus shedding and interrupting chains of transmission by social distancing and public masking are required.
Keywords: Covid-19; MERS; SARS; pandemic influenza; pre-symptomatic infection; viral shedding.
© 2020 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that there is no existing commercial or financial conflict of interest, in any way.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Review of SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and Influenza A Respiratory Viruses.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 11;11:552909. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.552909. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33013925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneity in transmissibility and shedding SARS-CoV-2 via droplets and aerosols.Elife. 2021 Apr 16;10:e65774. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65774. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33861198 Free PMC article.
-
From SARS and MERS to COVID-19: a brief summary and comparison of severe acute respiratory infections caused by three highly pathogenic human coronaviruses.Respir Res. 2020 Aug 27;21(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01479-w. Respir Res. 2020. PMID: 32854739 Free PMC article.
-
Why COVID-19 Transmission Is More Efficient and Aggressive Than Viral Transmission in Previous Coronavirus Epidemics?Biomolecules. 2020 Sep 11;10(9):1312. doi: 10.3390/biom10091312. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32933047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Comparison of pathological changes and pathogenic mechanisms caused by H1N1 influenza virus, highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza virus, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and 2019-nCoV].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2020 May 8;49(5):511-516. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112151-20200301-00155. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32392945 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Single domain antibodies derived from ancient animals as broadly neutralizing agents for SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses.Biomed Eng Adv. 2022 Dec;4:100054. doi: 10.1016/j.bea.2022.100054. Epub 2022 Sep 18. Biomed Eng Adv. 2022. PMID: 36158162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative highlights on MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV-1, SARS-CoV-2, and NEO-CoV.EXCLI J. 2022 Sep 29;21:1245-1272. doi: 10.17179/excli2022-5355. eCollection 2022. EXCLI J. 2022. PMID: 36483910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic infection in Coronavirus Disease 2019 pandemic.Med Rev (2021). 2022 Feb 24;2(1):66-88. doi: 10.1515/mr-2021-0034. eCollection 2022 Feb 1. Med Rev (2021). 2022. PMID: 35658110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of Current COVID-19 Diagnostics and Opportunities for Further Development.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 May 7;8:615099. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.615099. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34026773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoarchitectonics for synergistic activity of multimetallic nanohybrids as a possible approach for antimicrobial resistance (AMR).J Biol Inorg Chem. 2024 Aug;29(5):477-498. doi: 10.1007/s00775-024-02066-w. Epub 2024 Jul 12. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 38995397 Review.
References
-
- WHO . Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS‐CoV) – Qatar 2020. https://www.who.int/csr/don/12-march-2020-mers-qatar/en/. Accessed 30 March 2020.
-
- WHO . Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) situation report – 72 [Organization website]. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2.... Accessed 30 July, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

