High-speed super-resolution imaging of rotationally symmetric structures using SPEED microscopy and 2D-to-3D transformation
- PMID: 33318694
- PMCID: PMC9382854
- DOI: 10.1038/s41596-020-00440-x
High-speed super-resolution imaging of rotationally symmetric structures using SPEED microscopy and 2D-to-3D transformation
Abstract
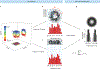
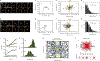
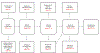
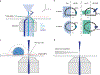
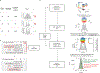
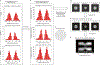
Various super-resolution imaging techniques have been developed to break the diffraction-limited resolution of light microscopy. However, it still remains challenging to obtain three-dimensional (3D) super-resolution information of structures and dynamic processes in live cells at high speed. We recently developed high-speed single-point edge-excitation sub-diffraction (SPEED) microscopy and its two-dimensional (2D)-to-3D transformation algorithm to provide an effective approach to achieving 3D sub-diffraction-limit information in subcellular structures and organelles that have rotational symmetry. In contrast to most other 3D super-resolution microscopy or 3D particle-tracking microscopy approaches, SPEED microscopy does not depend on complex optical components and can be implemented onto a standard inverted epifluorescence microscope. SPEED microscopy is specifically designed to obtain 2D spatial locations of individual immobile or moving fluorescent molecules inside sub-micrometer biological channels or cavities at high spatiotemporal resolution. After data collection, post-localization 2D-to-3D transformation is applied to obtain 3D super-resolution structural and dynamic information. The complete protocol, including cell culture and sample preparation (6-7 d), SPEED imaging (4-5 h), data analysis and validation through simulation (5-13 h), takes ~9 d to complete.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
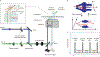

Similar articles
-
Obtaining 3D super-resolution images by utilizing rotationally symmetric structures and 2D-to-3D transformation.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Feb 8;21:1424-1432. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.02.008. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 36824228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Super-resolution SPEED Microscopy in the Study of Cellular Dynamics.Chem Biomed Imaging. 2023 Jun 24;1(4):356-371. doi: 10.1021/cbmi.3c00036. eCollection 2023 Jul 24. Chem Biomed Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37501792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D Tracking-Free Approach for Obtaining 3D Super-Resolution Information in Rotationally Symmetric Biostructures.J Phys Chem B. 2019 Jun 20;123(24):5107-5120. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.9b02979. Epub 2019 Jun 10. J Phys Chem B. 2019. PMID: 31117612 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid high resolution 3D imaging of expanded biological specimens with lattice light sheet microscopy.Methods. 2020 Mar 1;174:11-19. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2019.04.006. Epub 2019 Apr 9. Methods. 2020. PMID: 30978505
-
High-SPEED super-resolution SPEED microscopy to study primary cilium signaling in vivo.Methods Cell Biol. 2023;176:181-197. doi: 10.1016/bs.mcb.2022.12.016. Epub 2023 Jan 27. Methods Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37164537
Cited by
-
Distinct roles of nuclear basket proteins in directing the passage of mRNA through the nuclear pore.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Sep 14;118(37):e2015621118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2015621118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34504007 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Cellular Gateways: Unraveling the Secrets of Disordered Proteins within Live Nuclear Pores.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 9:rs.3.rs-3504130. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3504130/v1. Res Sq. 2024. PMID: 38260360 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Selective Degradation and Quantification of Nucleoporins in the Nuclear Pore by Auxin-Inducible Degrons and Single-Molecule Microscopy.Curr Protoc. 2022 Sep;2(9):e520. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.520. Curr Protoc. 2022. PMID: 36063146 Free PMC article.
-
Spelling out the roles of individual nucleoporins in nuclear export of mRNA.Nucleus. 2022 Dec;13(1):170-193. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2022.2076965. Nucleus. 2022. PMID: 35593254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obtaining 3D super-resolution images by utilizing rotationally symmetric structures and 2D-to-3D transformation.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Feb 8;21:1424-1432. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.02.008. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 36824228 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Related links
References
-
- Abbe E Beiträge zur Theorie des Mikroskops und der mikroskopischen Wahrnehmung. Archiv für Mik-roskopische Anatomie 9, 413–468 (1873).
-
- Mockl L, Lamb DC & Brauchle C Super-resolved fluorescence microscopy: Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2014 for Eric Betzig, Stefan Hell, and William E. Moerner. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 53, 13972–13977 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Schermelleh L et al. Super-resolution microscopy demystified. Nat. Cell Biol. 21, 72–84 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

