A prospective study to explore the relationship between MTHFR C677T genotype, physiological folate levels, and postpartum psychopathology in at-risk women
- PMID: 33315905
- PMCID: PMC7735580
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243936
A prospective study to explore the relationship between MTHFR C677T genotype, physiological folate levels, and postpartum psychopathology in at-risk women
Abstract
Background: The etiology of postpartum psychopathologies are not well understood, but folate metabolism pathways are of potential interest. Demands for folate increase dramatically during pregnancy, low folate level has been associated with psychiatric disorders, and supplementation may improve symptomatology. The MTHFR C677T variant influences folate metabolism and has been implicated in depression during pregnancy.
Objective: To conduct a prospective longitudinal study to explore the relationship between MTHFR C677T genotype, folate levels, and postpartum psychopathology in at-risk women.
Hypothesis: In the first three months postpartum, folate will moderate a relationship between MTHFR genotype and depression, with TT homozygous women having more symptoms than CC homozygous women.
Methods: We recruited 365 pregnant women with a history of mood or psychotic disorder, and at 3 postpartum timepoints, administered the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS); Clinician-Administered Rating Scale for Mania (CARS-M) and the Positive and Negative Symptom Scale (PANSS) and drew blood for genotype/folate level analysis. We used robust linear regression to investigate interactions between genotype and folate level on the highest EPDS and CARS-M scores, and logistic regression to explore interactions with PANSS psychosis scores above/below cut-off.
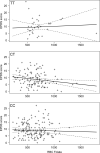
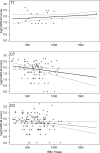
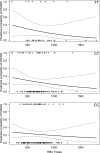
Results: There was no significant interaction effect between MTHFR genotype and folate level on highest EPDS (p = 0.36), but there was a significant interaction between genotype, folate level and log(CARS-M) (p = 0.02); post-hoc analyses revealed differences in the effect of folate level between CC/CT, and TT genotypes, with folate level in CC and CT having an inverse relationship with symptoms of mania, while there was no relationship in participants with TT genotype. There was no significant interaction between MTHFR genotype and folate level on the likelihood of meeting positive symptom criteria for psychosis on the PANSS (p = 0.86).
Discussion: These data suggest that perhaps there is a relationship between MTHFR C677T, folate level and some symptoms of postpartum psychopathology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation during pregnancy may protect against depression 21 months after pregnancy, an effect modified by MTHFR C677T genotype.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2012 Jan;66(1):97-103. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2011.136. Epub 2011 Jul 20. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2012. PMID: 21772318
-
Interactions between genetic variants involved in the folate metabolic pathway and serum lipid, homocysteine levels on the risk of recurrent spontaneous abortion.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Jun 15;18(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1083-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 31200713 Free PMC article.
-
Gene--nutrition interactions in coronary artery disease: correlation between the MTHFR C677T polymorphism and folate and homocysteine status in a Korean population.Thromb Res. 2006;117(5):501-6. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2005.04.009. Epub 2005 Jun 1. Thromb Res. 2006. PMID: 15935452
-
Assessing the association between the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) 677C>T polymorphism and blood folate concentrations: a systematic review and meta-analysis of trials and observational studies.Am J Clin Nutr. 2015 Jun;101(6):1286-94. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.114.099994. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25788000 Review.
-
The thermolabile variant of MTHFR is associated with depression in the British Women's Heart and Health Study and a meta-analysis.Mol Psychiatry. 2006 Apr;11(4):352-60. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001790. Mol Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16402130 Review.
Cited by
-
Postpartum Psychosis.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2023 Feb;25(2):65-72. doi: 10.1007/s11920-022-01406-4. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2023. PMID: 36637712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MTHFR 677TT is associated with decreased number of embryos and cumulative live birth rate in patients undergoing GnRHa short protocol: a retrospective study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2022 Mar 1;22(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12884-022-04506-4. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2022. PMID: 35232413 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howard L: Postnatal depression. American Family Physician 72, 2005

