HOX paralogs selectively convert binding of ubiquitous transcription factors into tissue-specific patterns of enhancer activation
- PMID: 33315856
- PMCID: PMC7769617
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009162
HOX paralogs selectively convert binding of ubiquitous transcription factors into tissue-specific patterns of enhancer activation
Abstract
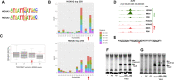
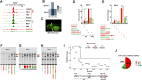
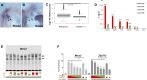
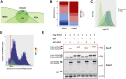
Gene expression programs determine cell fate in embryonic development and their dysregulation results in disease. Transcription factors (TFs) control gene expression by binding to enhancers, but how TFs select and activate their target enhancers is still unclear. HOX TFs share conserved homeodomains with highly similar sequence recognition properties, yet they impart the identity of different animal body parts. To understand how HOX TFs control their specific transcriptional programs in vivo, we compared HOXA2 and HOXA3 binding profiles in the mouse embryo. HOXA2 and HOXA3 directly cooperate with TALE TFs and selectively target different subsets of a broad TALE chromatin platform. Binding of HOX and tissue-specific TFs convert low affinity TALE binding into high confidence, tissue-specific binding events, which bear the mark of active enhancers. We propose that HOX paralogs, alone and in combination with tissue-specific TFs, generate tissue-specific transcriptional outputs by modulating the activity of TALE TFs at selected enhancers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
TALE transcription factors: Cofactors no more.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jan-Feb;152-153:76-84. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.11.015. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 36509674 Review.
-
Combinatorial action of NF-Y and TALE at embryonic enhancers defines distinct gene expression programs during zygotic genome activation in zebrafish.Dev Biol. 2020 Mar 15;459(2):161-180. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2019.12.003. Epub 2019 Dec 17. Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 31862379 Free PMC article.
-
Hoxa2 selectively enhances Meis binding to change a branchial arch ground state.Dev Cell. 2015 Feb 9;32(3):265-77. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.12.024. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Dev Cell. 2015. PMID: 25640223 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of distinct homeodomain DNA binding specificities to Drosophila embryonic mesodermal cell-specific gene expression programs.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 26;8(7):e69385. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069385. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23922708 Free PMC article.
-
To Be Specific or Not: The Critical Relationship Between Hox And TALE Proteins.Trends Genet. 2016 Jun;32(6):334-347. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2016.03.004. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Trends Genet. 2016. PMID: 27066866 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multimodal Hox5 activity generates motor neuron diversity.Commun Biol. 2024 Sep 17;7(1):1166. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06835-w. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39289460 Free PMC article.
-
A spatio-temporally constrained gene regulatory network directed by PBX1/2 acquires limb patterning specificity via HAND2.Nat Commun. 2023 Jul 6;14(1):3993. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39443-z. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37414772 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Regulation and Implications for Controlling Hox Gene Expression.J Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 10;10(1):4. doi: 10.3390/jdb10010004. J Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35076545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hox proteins interact to pattern neuronal subtypes in Caenorhabditis elegans males.Genetics. 2022 Apr 4;220(4):iyac010. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac010. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 35137058 Free PMC article.
-
Meis homeobox genes control progenitor competence in the retina.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Mar 23;118(12):e2013136118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2013136118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33723039 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

