Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicle-Mediated Cytosolic Delivery of Flagellin Triggers Host NLRC4 Canonical Inflammasome Signaling
- PMID: 33312172
- PMCID: PMC7708323
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.581165
Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicle-Mediated Cytosolic Delivery of Flagellin Triggers Host NLRC4 Canonical Inflammasome Signaling
Abstract
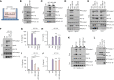
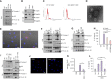
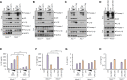
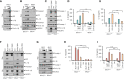
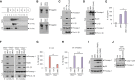
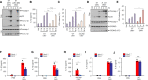
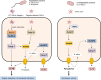
Bacteria-released components can modulate host innate immune response in the absence of direct host cell-bacteria interaction. In particular, bacteria-derived outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) were recently shown to activate host caspase-11-mediated non-canonical inflammasome pathway via deliverance of OMV-bound lipopolysaccharide. However, further precise understanding of innate immune-modulation by bacterial OMVs remains elusive. Here, we present evidence that flagellated bacteria-released OMVs can trigger NLRC4 canonical inflammasome activation via flagellin delivery to the cytoplasm of host cells. Salmonella typhimurium-derived OMVs caused a robust NLRC4-mediated caspase-1 activation and interleukin-1β secretion in macrophages in an endocytosis-dependent, but guanylate-binding protein-independent manner. Notably, OMV-associated flagellin is crucial for Salmonella OMV-induced inflammasome response. Flagellated Pseudomonas aeruginosa-released OMVs consistently promoted robust NLRC4 inflammasome activation, while non-flagellated Escherichia coli-released OMVs induced NLRC4-independent non-canonical inflammasome activation leading to NLRP3-mediated interleukin-1β secretion. Flagellin-deficient Salmonella OMVs caused a weak interleukin-1β production in a NLRP3-dependent manner. These findings indicate that Salmonella OMV triggers NLRC4 inflammasome activation via OMV-associated flagellin in addition to a mild induction of non-canonical inflammasome signaling via OMV-bound lipopolysaccharide. Intriguingly, flagellated Salmonella-derived OMVs induced more rapid inflammasome response than flagellin-deficient Salmonella OMV and non-flagellated Escherichia coli-derived OMVs. Supporting these in vitro results, Nlrc4-deficient mice showed significantly reduced interleukin-1β production after intraperitoneal challenge with Salmonella-released OMVs. Taken together, our results here propose that NLRC4 inflammasome machinery is a rapid sensor of bacterial OMV-bound flagellin as a host defense mechanism against bacterial pathogen infection.
Keywords: NLRC4; caspase-1; flagellin; host defense; inflammasome; interleukin-1; outer membrane vesicles.
Copyright © 2020 Yang, Hwang, Lee, Shin, Lee, Rhee and Yu.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of NLRC4 by flagellated bacteria triggers caspase-1-dependent and -independent responses to restrict Legionella pneumophila replication in macrophages and in vivo.J Immunol. 2011 Dec 15;187(12):6447-55. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003784. Epub 2011 Nov 11. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22079982
-
NLRP3 recruitment by NLRC4 during Salmonella infection.J Exp Med. 2016 May 30;213(6):877-85. doi: 10.1084/jem.20132234. Epub 2016 May 2. J Exp Med. 2016. PMID: 27139490 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase-11 activation in response to bacterial secretion systems that access the host cytosol.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(6):e1003400. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003400. Epub 2013 Jun 6. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23762026 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammasome-dependent Mechanisms Involved in Sensing and Restriction of Bacterial Replication.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2018;25:99-132. doi: 10.21775/cimb.025.099. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 28875942 Review.
-
Advances in Understanding Activation and Function of the NLRC4 Inflammasome.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 21;22(3):1048. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031048. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33494299 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Immunity and Host Defense.Immunol Invest. 2024 Jan;53(1):10-25. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2024.2312896. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Immunol Invest. 2024. PMID: 38348776 Review.
-
The Delivery of Extracellular "Danger" Signals to Cytosolic Sensors in Phagocytes.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 14;13:944142. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.944142. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35911757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influences of bacterial extracellular vesicles on macrophage immune functions.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 May 30;14:1411196. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1411196. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38873097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitors of Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 23;13:835058. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.835058. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35283837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review: Protective Immunity and Immunopathology of Ehrlichiosis.Zoonoses (Burlingt). 2022 Jan 6;2(1):10.15212/zoonoses-2022-0009. doi: 10.15212/zoonoses-2022-0009. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Zoonoses (Burlingt). 2022. PMID: 35876763 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

