Changes in oxidation-antioxidation function on the thymus of chickens infected with reticuloendotheliosis virus
- PMID: 33308224
- PMCID: PMC7731740
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-020-02708-6
Changes in oxidation-antioxidation function on the thymus of chickens infected with reticuloendotheliosis virus
Abstract
Background: Reticuloendotheliosis virus (REV) is a retrovirus that causes severe immunosuppression in poultry. Animals grow slowly under conditions of oxidative stress. In addition, long-term oxidative stress can impair immune function, as well as accelerate aging and death. This study aimed to elucidate the pathogenesis of REV from the perspective of changes in oxidative-antioxidative function following REV infection.
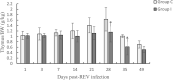
Methods: A total of 80 one-day-old specific pathogen free (SPF) chickens were randomly divided into a control group (Group C) and an REV-infected group (Group I). The chickens in Group I received intraperitoneal injections of REV with 104.62/0.1 mL TCID50. Thymus was collected on day 1, 3, 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, and 49 for histopathology and assessed the status of oxidative stress.
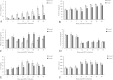
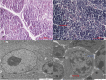
Results: In chickens infected with REV, the levels of H2O2 and MDA in the thymus increased, the levels of TAC, SOD, CAT, and GPx1 decreased, and there was a reduction in CAT and Gpx1 mRNA expression compared with the control group. The thymus index was also significantly reduced. Morphological analysis showed that REV infection caused an increase in the thymic reticular endothelial cells, inflammatory cell infiltration, mitochondrial swelling, and nuclear damage.
Conclusions: These results indicate that an increase in oxidative stress enhanced lipid peroxidation, markedly decreased antioxidant function, caused thymus atrophy, and immunosuppression in REV-infected chickens.
Keywords: Histopathological and ultrastructural changes; Immunosuppression; Oxidation antioxidant imbalance; Reticuloendotheliosis virus; Thymus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

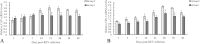
Similar articles
-
Synergetic effects of subgroup J avian leukosis virus and reticuloendotheliosis virus co-infection on growth retardation and immunosuppression in SPF chickens.Vet Microbiol. 2014 Aug 27;172(3-4):425-31. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.06.025. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Vet Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25042879
-
Changes in apoptosis, proliferation and T lymphocyte subtype on thymic cells of SPF chickens infected with reticuloendotheliosis virus.Mol Immunol. 2019 Jul;111:87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2019.04.003. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Mol Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31048099
-
Isolation and pathogenicity testing of avian reticuloendotheliosis virus from layer chickens in China.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2020 May;32(3):389-393. doi: 10.1177/1040638720914881. Epub 2020 Apr 1. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2020. PMID: 32233842 Free PMC article.
-
Avian retroviruses.Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 1997 Mar;13(1):71-85. doi: 10.1016/s0749-0720(15)30365-0. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 1997. PMID: 9071747 Review.
-
The avian reticuloendotheliosis virus, strain T (REV).Zhonghua Min Guo Wei Sheng Wu Ji Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 1983 Sep;16(3):217-75. Zhonghua Min Guo Wei Sheng Wu Ji Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 1983. PMID: 6094120 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Vitamin A on Antioxidant and Intestinal Barrier Function of Broilers Co-Infected with Coccidia and Clostridium perfringens.Animals (Basel). 2022 Dec 5;12(23):3431. doi: 10.3390/ani12233431. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36496951 Free PMC article.
-
Infection-Associated Thymic Atrophy.Front Immunol. 2021 May 25;12:652538. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.652538. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34113341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tandem Mass Tag-Based Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Chicken Bursa of Fabricius Infected With Reticuloendotheliosis Virus.Front Vet Sci. 2021 May 25;8:666512. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.666512. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34113672 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the genetic characteristics of copy number variations in experimental specific pathogen-free ducks using whole-genome resequencing.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jan 2;25(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09928-8. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38166615 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bohls RL, Linares JA, Gross SL, Ferro PJ, Silvy NJ, Collisson EW. Phylogenetic analyses indicate little variation among reticuloendotheliosis viruses infecting avian species, including the endangered Attwater’s prairie chicken. Virus Res. 2006;119(2):187–94. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2006.01.011. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

