Blockade of EIF5A hypusination limits colorectal cancer growth by inhibiting MYC elongation
- PMID: 33303756
- PMCID: PMC7729396
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-03174-6
Blockade of EIF5A hypusination limits colorectal cancer growth by inhibiting MYC elongation
Abstract
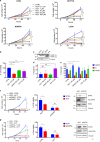
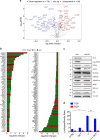
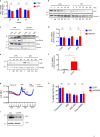
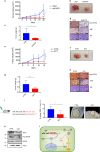
Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 5A (EIF5A) is a translation factor regulated by hypusination, a unique posttranslational modification catalyzed by deoxyhypusine synthetase (DHPS) and deoxyhypusine hydroxylase (DOHH) starting from the polyamine spermidine. Emerging data are showing that hypusinated EIF5A regulates key cellular processes such as autophagy, senescence, polyamine homeostasis, energy metabolism, and plays a role in cancer. However, the effects of EIF5A inhibition in preclinical cancer models, the mechanism of action, and specific translational targets are still poorly understood. We show here that hypusinated EIF5A promotes growth of colorectal cancer (CRC) cells by directly regulating MYC biosynthesis at specific pausing motifs. Inhibition of EIF5A hypusination with the DHPS inhibitor GC7 or through lentiviral-mediated knockdown of DHPS or EIF5A reduces the growth of various CRC cells. Multiplex gene expression analysis reveals that inhibition of hypusination impairs the expression of transcripts regulated by MYC, suggesting the involvement of this oncogene in the observed effect. Indeed, we demonstrate that EIF5A regulates MYC elongation without affecting its mRNA content or protein stability, by alleviating ribosome stalling at five distinct pausing motifs in MYC CDS. Of note, we show that blockade of the hypusination axis elicits a remarkable growth inhibitory effect in preclinical models of CRC and significantly reduces the size of polyps in APCMin/+ mice, a model of human familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). Together, these data illustrate an unprecedented mechanism, whereby the tumor-promoting properties of hypusinated EIF5A are linked to its ability to regulate MYC elongation and provide a rationale for the use of DHPS/EIF5A inhibitors in CRC therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synergistic drug combination GC7/DFMO suppresses hypusine/spermidine-dependent eIF5A activation and induces apoptotic cell death in neuroblastoma.Biochem J. 2018 Jan 31;475(2):531-545. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170597. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 29295892
-
The Many Faces of Hypusinated eIF5A: Cell Context-Specific Effects of the Hypusine Circuit and Implications for Human Health.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 26;25(15):8171. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158171. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined inhibition of polyamine metabolism and eIF5A hypusination suppresses colorectal cancer growth through a converging effect on MYC translation.Cancer Lett. 2023 Apr 10;559:216120. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216120. Epub 2023 Mar 8. Cancer Lett. 2023. PMID: 36893894
-
Recessive Rare Variants in Deoxyhypusine Synthase, an Enzyme Involved in the Synthesis of Hypusine, Are Associated with a Neurodevelopmental Disorder.Am J Hum Genet. 2019 Feb 7;104(2):287-298. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.12.017. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Am J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 30661771 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the polyamine-hypusine circuit for the prevention and treatment of cancer.Amino Acids. 2016 Oct;48(10):2353-62. doi: 10.1007/s00726-016-2275-3. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Amino Acids. 2016. PMID: 27357307 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Narrative Review: Immunometabolic Interactions of Host-Gut Microbiota and Botanical Active Ingredients in Gastrointestinal Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 22;25(16):9096. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169096. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyamines: their significance for maintaining health and contributing to diseases.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Dec 4;21(1):348. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01373-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 38049863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutamine-derived aspartate is required for eIF5A hypusination-mediated translation of HIF-1α to induce the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages.Exp Mol Med. 2024 May;56(5):1123-1136. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01214-1. Epub 2024 May 1. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38689086 Free PMC article.
-
EIF5A expression and its role as a potential diagnostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cancer. 2021 Jun 11;12(16):4774-4779. doi: 10.7150/jca.58168. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34234848 Free PMC article.
-
Translation factor eIF5a is essential for IFNγ production and cell cycle regulation in primary CD8+ T lymphocytes.Nat Commun. 2022 Dec 17;13(1):7796. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35252-y. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36528626 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

