Argonaute NRDE-3 and MBT domain protein LIN-61 redundantly recruit an H3K9me3 HMT to prevent embryonic lethality and transposon expression
- PMID: 33303642
- PMCID: PMC7778263
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.344234.120
Argonaute NRDE-3 and MBT domain protein LIN-61 redundantly recruit an H3K9me3 HMT to prevent embryonic lethality and transposon expression
Abstract
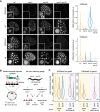
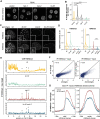
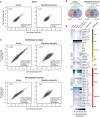
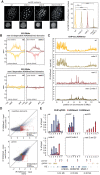
The establishment and maintenance of chromatin domains shape the epigenetic memory of a cell, with the methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me) defining transcriptionally silent heterochromatin. We show here that the C. elegans SET-25 (SUV39/G9a) histone methyltransferase (HMT), which catalyzes H3K9me1, me2 and me3, can establish repressed chromatin domains de novo, unlike the SETDB1 homolog MET-2. Thus, SET-25 is needed to silence novel insertions of RNA or DNA transposons, and repress tissue-specific genes de novo during development. We identify two partially redundant pathways that recruit SET-25 to its targets. One pathway requires LIN-61 (L3MBTL2), which uses its four MBT domains to bind the H3K9me2 deposited by MET-2. The second pathway functions independently of MET-2 and involves the somatic Argonaute NRDE-3 and small RNAs. This pathway targets primarily highly conserved RNA and DNA transposons. These redundant SET-25 targeting pathways (MET-2-LIN-61-SET-25 and NRDE-3-SET-25) ensure repression of intact transposons and de novo insertions, while MET-2 can act alone to repress simple and satellite repeats. Removal of both pathways in the met-2;nrde-3 double mutant leads to the loss of somatic H3K9me2 and me3 and the synergistic derepression of transposons in embryos, strongly elevating embryonic lethality.
Keywords: Argonaute; HMT; LIN-61; MBT domain proteins; MET-2; NRDE-3; SET-25; heterochromatin; histone methyltransferases (HMTs); transposon silencing.
© 2021 Padeken et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synergistic lethality between BRCA1 and H3K9me2 loss reflects satellite derepression.Genes Dev. 2019 Apr 1;33(7-8):436-451. doi: 10.1101/gad.322495.118. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Genes Dev. 2019. PMID: 30804228 Free PMC article.
-
H3K9me2/3 binding of the MBT domain protein LIN-61 is essential for Caenorhabditis elegans vulva development.PLoS Genet. 2011 Mar;7(3):e1002017. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002017. Epub 2011 Mar 17. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21437264 Free PMC article.
-
Unique roles for histone H3K9me states in RNAi and heritable silencing of transcription.Nature. 2017 Jul 27;547(7664):463-467. doi: 10.1038/nature23267. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28682306 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of H3K9-methylated heterochromatin and its functions in tissue differentiation and maintenance.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Sep;23(9):623-640. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00483-w. Epub 2022 May 13. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35562425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repressive Chromatin in Caenorhabditis elegans: Establishment, Composition, and Function.Genetics. 2018 Feb;208(2):491-511. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300386. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29378810 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
H3K9me1/2 methylation limits the lifespan of daf-2 mutants in C. elegans.Elife. 2022 Sep 20;11:e74812. doi: 10.7554/eLife.74812. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36125117 Free PMC article.
-
The functions of SET domain bifurcated histone lysine methyltransferase 1 (SETDB1) in biological process and disease.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2023 Dec 7;16(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s13072-023-00519-1. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2023. PMID: 38057834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coordinated maintenance of H3K36/K27 methylation by histone demethylases preserves germ cell identity and immortality.Cell Rep. 2021 Nov 23;37(8):110050. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110050. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34818537 Free PMC article.
-
XOL-1 regulates developmental timing by modulating the H3K9 landscape in C. elegans early embryos.PLoS Genet. 2024 Aug 15;20(8):e1011238. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011238. eCollection 2024 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 39146391 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Argonaute protein NRDE-3 switches small RNA partners during embryogenesis to mediate temporal-specific gene regulatory activity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 17:2024.07.29.605686. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.29.605686. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39131395 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
