Transport of L-Arginine Related Cardiovascular Risk Markers
- PMID: 33302555
- PMCID: PMC7764698
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9123975
Transport of L-Arginine Related Cardiovascular Risk Markers
Abstract
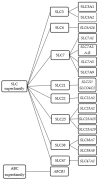
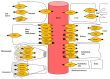
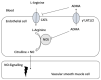
L-arginine and its derivatives, asymmetric and symmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA and SDMA) and L-homoarginine, have emerged as cardiovascular biomarkers linked to cardiovascular outcomes and various metabolic and functional pathways such as NO-mediated endothelial function. Cellular uptake and efflux of L-arginine and its derivatives are facilitated by transport proteins. In this respect the cationic amino acid transporters CAT1 and CAT2 (SLC7A1 and SLC7A2) and the system y+L amino acid transporters (SLC7A6 and SLC7A7) have been most extensively investigated, so far, but the number of transporters shown to mediate the transport of L-arginine and its derivatives is constantly increasing. In the present review we assess the growing body of evidence regarding the function, expression, and clinical relevance of these transporters and their possible relation to cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: ADMA; L-arginine; L-homoarginine; SDMA; transport.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interaction of the cardiovascular risk marker asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) with the human cationic amino acid transporter 1 (CAT1).J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012 Sep;53(3):392-400. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.06.002. Epub 2012 Jun 15. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22705145
-
The prognostic biomarker L-homoarginine is a substrate of the cationic amino acid transporters CAT1, CAT2A and CAT2B.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 6;7(1):4767. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04965-2. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28684763 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA), symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA) and homoarginine (hArg): the ADMA, SDMA and hArg paradoxes.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018 Jan 4;17(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0656-x. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018. PMID: 29301528 Free PMC article.
-
Arginine Derivatives in Cerebrovascular Diseases: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 5;21(5):1798. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051798. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32150996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxic Dimethylarginines: Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) and Symmetric Dimethylarginine (SDMA).Toxins (Basel). 2017 Mar 6;9(3):92. doi: 10.3390/toxins9030092. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28272322 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of asymmetric dimethylarginine with the pathological process of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn.Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Jan 15;24(1):54-59. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2108145. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35177176 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Nitric oxide metabolites: associations with cardiovascular biomarkers and clinical parameters in patients with HFpEF.ESC Heart Fail. 2022 Dec;9(6):3961-3972. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14116. Epub 2022 Aug 18. ESC Heart Fail. 2022. PMID: 35979962 Free PMC article.
-
Arginine Signaling and Cancer Metabolism.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 15;13(14):3541. doi: 10.3390/cancers13143541. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34298755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and CPAP Treatment on the Bioavailability of Erythrocyte and Plasma Nitric Oxide.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 9;19(22):14719. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192214719. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36429438 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes from HPV-16 E7-pulsed dendritic cells prevent the migration, M1 polarization, and inflammation of macrophages in cervical cancer by regulating catalase 2 (CAT2).Ann Transl Med. 2022 Feb;10(4):217. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-6998. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35280390 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Cardiovascular Diseases. [(accessed on 10 June 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

