Protein synthesis inhibitors stimulate MondoA transcriptional activity by driving an accumulation of glucose 6-phosphate
- PMID: 33292639
- PMCID: PMC7718662
- DOI: 10.1186/s40170-020-00233-6
Protein synthesis inhibitors stimulate MondoA transcriptional activity by driving an accumulation of glucose 6-phosphate
Abstract
Background: Protein synthesis is regulated by the availability of amino acids, the engagement of growth factor signaling pathways, and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels sufficient to support translation. Crosstalk between these inputs is extensive, yet other regulatory mechanisms remain to be characterized. For example, the translation initiation inhibitor rocaglamide A (RocA) induces thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP). TXNIP is a negative regulator of glucose uptake; thus, its induction by RocA links translation to the availability of glucose. MondoA is the principal regulator of glucose-induced transcription, and its activity is triggered by the glycolytic intermediate, glucose 6-phosphate (G6P). MondoA responds to G6P generated by cytoplasmic glucose and mitochondrial ATP (mtATP), suggesting a critical role in the cellular response to these energy sources. TXNIP expression is entirely dependent on MondoA; therefore, we investigated how protein synthesis inhibitors impact its transcriptional activity.
Methods: We investigated how translation regulates MondoA activity using cell line models and loss-of-function approaches. We examined how protein synthesis inhibitors effect gene expression and metabolism using RNA-sequencing and metabolomics, respectively. The biological impact of RocA was evaluated using cell lines and patient-derived xenograft organoid (PDxO) models.
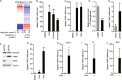
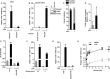
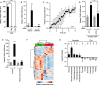
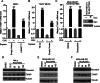
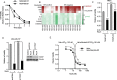
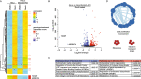
Results: We discovered that multiple protein synthesis inhibitors, including RocA, increase TXNIP expression in a manner that depends on MondoA, a functional electron transport chain and mtATP synthesis. Furthermore, RocA and cycloheximide increase mtATP and G6P levels, respectively, and TXNIP induction depends on interactions between the voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC) and hexokinase (HK), which generates G6P. RocA treatment impacts the regulation of ~ 1200 genes, and ~ 250 of those genes are MondoA-dependent. RocA treatment is cytotoxic to triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell lines and shows preferential cytotoxicity against estrogen receptor negative (ER-) PDxO breast cancer models. Finally, RocA-driven cytotoxicity is partially dependent on MondoA or TXNIP.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that protein synthesis inhibitors rewire metabolism, resulting in an increase in mtATP and G6P, the latter driving MondoA-dependent transcriptional activity. Further, MondoA is a critical component of the cellular transcriptional response to RocA. Our functional assays suggest that RocA or similar translation inhibitors may show efficacy against ER- breast tumors and that the levels of MondoA and TXNIP should be considered when exploring these potential treatment options.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Rocaglamide reprograms glucose metabolism in erythroleukemic cells via c-MYC transcriptional regulation of TXNIP and HK2.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jan 13;339:119145. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119145. Epub 2024 Nov 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39580129
-
Defining the optimum strategy for identifying adults and children with coeliac disease: systematic review and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Oct;26(44):1-310. doi: 10.3310/ZUCE8371. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36321689 Free PMC article.
-
Qualitative evidence synthesis informing our understanding of people's perceptions and experiences of targeted digital communication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 23;10(10):ED000141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000141. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31643081 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions to reduce harm from continued tobacco use.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 13;10(10):CD005231. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005231.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27734465 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein in Cancer and Diabetes.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022 May;36(13-15):1001-1022. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0038. Epub 2021 Oct 7. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022. PMID: 34384271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TXNIP: A Double-Edged Sword in Disease and Therapeutic Outlook.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Apr 11;2022:7805115. doi: 10.1155/2022/7805115. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35450411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Normal and Neoplastic Growth Suppression by the Extended Myc Network.Cells. 2022 Feb 21;11(4):747. doi: 10.3390/cells11040747. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35203395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reversible translocation of acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) between the endoplasmic reticulum and vesicular structures.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Nov 10;10:1258799. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1258799. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38028547 Free PMC article.
-
TXNIP loss expands Myc-dependent transcriptional programs by increasing Myc genomic binding.PLoS Biol. 2023 Mar 17;21(3):e3001778. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001778. eCollection 2023 Mar. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 36930677 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

