Skin Resident γδ T Cell Function and Regulation in Wound Repair
- PMID: 33291435
- PMCID: PMC7729629
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21239286
Skin Resident γδ T Cell Function and Regulation in Wound Repair
Abstract
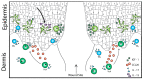
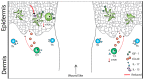
The skin is a critical barrier that protects against damage and infection. Within the epidermis and dermis reside γδ T cells that play a variety of key roles in wound healing and tissue homeostasis. Skin-resident γδ T cells require T cell receptor (TCR) ligation, costimulation, and cytokine reception to mediate keratinocyte activity and inflammatory responses at the wound site for proper wound repair. While both epidermal and dermal γδ T cells regulate inflammatory responses in wound healing, the timing and factors produced are distinct. In the absence of growth factors, cytokines, and chemokines produced by γδ T cells, wound repair is negatively impacted. This disruption in γδ T cell function is apparent in metabolic diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. This review provides the current state of knowledge on skin γδ T cell activation, regulation, and function in skin homeostasis and repair in mice and humans. As we uncover more about the complex roles played by γδ T cells in wound healing, novel targets can be discovered for future clinical therapies.
Keywords: DETC; T cell; chemokine; cytokine; dermis; diabetes; epidermis; obesity; wound repair; γδ T cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A keratinocyte-responsive gamma delta TCR is necessary for dendritic epidermal T cell activation by damaged keratinocytes and maintenance in the epidermis.J Immunol. 2004 Mar 15;172(6):3573-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.6.3573. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15004158
-
Functions of Vγ4 T Cells and Dendritic Epidermal T Cells on Skin Wound Healing.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 4;9:1099. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01099. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29915573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of skin cell homeostasis by gamma delta T cells.Front Biosci. 2004 Sep 1;9:2640-51. doi: 10.2741/1423. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 15358587 Review.
-
Dysfunctional γδ T cells contribute to impaired keratinocyte homeostasis in mouse models of obesity.J Invest Dermatol. 2011 Dec;131(12):2409-18. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.241. Epub 2011 Aug 11. J Invest Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 21833015 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal T cells and wound healing.J Immunol. 2010 May 15;184(10):5423-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902733. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20483798 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gamma delta T-cell reconstitution after allogeneic HCT: A platform for cell therapy.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 29;13:971709. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.971709. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36105821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunology of Acute and Chronic Wound Healing.Biomolecules. 2021 May 8;11(5):700. doi: 10.3390/biom11050700. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34066746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Immunological Impact of IL-1 Family Cytokines on the Epidermal Barrier.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 23;12:808012. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.808012. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skin immunity in wound healing and cancer.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 16;14:1060258. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1060258. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37398649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatiotemporal orchestration of macrophage activation trajectories by Vγ4 T cells during skin wound healing.iScience. 2024 Mar 21;27(4):109545. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109545. eCollection 2024 Apr 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38617557 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

