Dynamic changes of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts breast cancer prognosis
- PMID: 33287745
- PMCID: PMC7720486
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-020-07700-9
Dynamic changes of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts breast cancer prognosis
Abstract
Background: We aimed to identify whether neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) are more useful predictors after initial intention to treat than at the time of diagnosis.
Methods: We collected the medical data of 533 patients. The results of the peripheral blood sampling before the primary treatments were labeled as initial cohort, and those obtained between 24 and 36 months after initial treatment were defined as the 2nd cohort. Delayed metastasis has been defined as distant metastasis 2 years after treatment, and survival outcome was estimated and compared across groups.
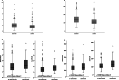
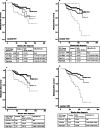
Results: Median follow-up duration was 74 months (24-162 months), and 53 patients experienced delayed metastasis. In univariate analysis, metastasis-free survival, patient age at diagnosis, tumor size, axillary lymph node metastasis, HER-2 status, initial NLR and PLR, and 2nd NLR and PLR were found to be significantly associated with delayed metastasis. However, in multivariate analysis, only the 2nd NLR and PLR were found to be significantly associated with delayed metastasis, excluding initial NLR and PLR. Metastasis-free survival was analyzed through the pattern changes of NLR or PLR. The results revealed that patients with continued low NLR and PLR values at pre- and post-treatment (low initial values and 2nd values) showed a significantly better prognosis than those with a change in value or continued high NLR and PLR.
Conclusions: We identified that patients with persistent high NLR and PLR after initial treatment have significant worse prognosis in terms of late metastasis. Therefore, these results suggest that NLR and PLR are more useful in predicting prognosis post-treatment.
Keywords: Biomarker; Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio; Prognostic factor.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there is no actual or potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Are neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and platelet/lymphocyte ratio associated with prognosis in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer receiving adjuvant trastuzumab?J BUON. 2015 May-Jun;20(3):714-22. J BUON. 2015. PMID: 26214622
-
Blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios are independent prognostic factors for surgically resected gastrointestinal stromal tumors.Surgery. 2016 Apr;159(4):1146-56. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2015.10.021. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Surgery. 2016. PMID: 26688506
-
Preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio before platelet-lymphocyte ratio predicts clinical outcome in patients with cervical cancer treated with initial radical surgery.Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2014 Sep;24(7):1319-25. doi: 10.1097/IGC.0000000000000219. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25033256
-
Prognostic Significance of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Oncologic Outcomes of Esophageal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Ann Surg Oncol. 2016 Feb;23(2):646-54. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4869-5. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26416715 Review.
-
Significance of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) and Platelet Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR) in Diabetic Foot Ulcer and Potential New Therapeutic Targets.Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2024 Jun;23(2):205-216. doi: 10.1177/15347346211057742. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2024. PMID: 34791913 Review.
Cited by
-
Leveraging the Dynamic Immune Environment Triad in Patients with Breast Cancer: Tumour, Lymph Node, and Peripheral Blood.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 17;14(18):4505. doi: 10.3390/cancers14184505. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil‑to‑lymphocyte ratio before each chemotherapy line predicts clinical outcomes in patients with unresectable gastric cancer.Oncol Lett. 2023 Jan 27;25(3):98. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.13684. eCollection 2023 Mar. Oncol Lett. 2023. PMID: 36817039 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation-based Prognostic Score as a Prognostic Biomarker in Patients With Recurrent and/or Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated With Nivolumab Therapy.In Vivo. 2022 Mar-Apr;36(2):907-917. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12780. In Vivo. 2022. PMID: 35241549 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is associated with poorer progression-free survival in unresectable stage III NSCLC treated with consolidation durvalumab.Thorac Cancer. 2022 Nov;13(21):3058-3062. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14646. Epub 2022 Sep 16. Thorac Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36111516 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in neutrophile-to-lymphocyte ratio as predictive and prognostic biomarker in metastatic prostate cancer treated with taxane-based chemotherapy.Discov Oncol. 2022 Dec 15;13(1):140. doi: 10.1007/s12672-022-00603-0. Discov Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36522513 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

