PI3K inhibition sensitizes EGFR wild-type NSCLC cell lines to erlotinib chemotherapy
- PMID: 33235618
- PMCID: PMC7678642
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.9441
PI3K inhibition sensitizes EGFR wild-type NSCLC cell lines to erlotinib chemotherapy
Abstract
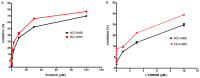
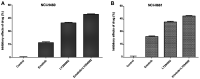
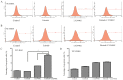
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) bring significant benefits for patients with cancers harboring epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations. However, after treatment for a certain period, most patients ultimately acquire resistance. Numerous studies indicated that PI3K has an important role in tumor cell growth and drug sensitivity. Furthermore, inhibition of PI3K may lead to sensitization of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells to EGFR-TKIs. The aim of the present study was to explore whether LY294002, an inhibitor of PI3K, is able to improve the sensitivity of NSCLC cell lines with wild-type EGFR to the EGFR-TKI erlotinib. An MTT assay was used to examine the effect of combined treatment with LY294002 and erlotinib on cell survival of two EGFR wild-type NSCLC cell lines, NCI-H661 and NCI-H460. Furthermore, flow cytometry was used to assess apoptosis in NCI-H661 and NCI-H460 cells after treatment with erlotinib and LY294002. In addition, the expression of downstream proteins was detected by western blot analysis. The results indicated that the number of viable NCI-H661 and NCI-H460 cells was dose-dependently reduced by erlotinib or LY294002. Compared to treatment with erlotinib alone, the cell apoptosis was enhanced if combined treatment of erlotinib and LY294002 was performed in NCI-H661 cells. Furthermore, combination treatment of erlotinib and LY294002 resulted in a significant reduction of phosphorylated p70S6K levels in NCI-H661 [PI3K catalytic subunit alpha (PI3KCA) wild-type] cells. However, this phenomenon was not observed in the NCI-H460 cell line (PIK3CA mutant-type). In conclusion, the present study indicated that inhibition of PI3K may have the potential to improve the sensitivity of NSCLC cells to an EGFR-TKI. However, the therapeutic effect may depend on the mutation status of PIK3CA.
Keywords: PI3K inhibitor; epidermal growth factor receptor; inhibitor; non-small cell lung cancer; p70S6K.
Copyright: © Zhou et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combined inhibition of the EGFR and mTOR pathways in EGFR wild-type non-small cell lung cancer cell lines with different genetic backgrounds.Oncol Rep. 2013 Jun;29(6):2486-92. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2357. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23525575
-
The pan-HDAC inhibitor panobinostat acts as a sensitizer for erlotinib activity in EGFR-mutated and -wildtype non-small cell lung cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2015 Dec 16;15:947. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1967-5. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26675484 Free PMC article.
-
Polo-like kinase 1 inhibition diminishes acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer with T790M mutations.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):47998-48010. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10332. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27384992 Free PMC article.
-
Erlotinib or gefitinib for the treatment of relapsed platinum pretreated non-small cell lung cancer and ovarian cancer: a systematic review.Drug Resist Updat. 2011 Jun;14(3):177-90. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2011.02.004. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Drug Resist Updat. 2011. PMID: 21435938 Review.
-
Neoadjuvant and adjuvant epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) therapy for lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015 Feb;4(1):82-93. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2014.11.08. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25806348 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LPCAT1 promotes gefitinib resistance via upregulation of the EGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in lung adenocarcinoma.J Cancer. 2022 Mar 21;13(6):1837-1847. doi: 10.7150/jca.66126. eCollection 2022. J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35399731 Free PMC article.
-
NSAIDs Overcome PIK3CA Mutation-Mediated Resistance to EGFR Inhibition in Head and Neck Cancer Preclinical Models.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 20;14(3):506. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030506. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35158773 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Origins of EGFR-Driven Lung Cancer Cells Determine Sensitivity to Therapy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Nov;8(22):e2101999. doi: 10.1002/advs.202101999. Epub 2021 Oct 7. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34622577 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment with Anlotinib After Chemotherapy and EGFR-TKI Resistance in Lung Adenosquamous Carcinoma with Concurrent EGFR and PIK3CA Mutations: A Case Report and Literature Review.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Sep 9;13:7047-7053. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S326094. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34526820 Free PMC article.
-
[Targeted Therapy and Mechanism of Drug Resistance in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene Mutation].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022 Mar 20;25(3):183-192. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2022.101.05. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35340161 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Mouradian M, Kikawa KD, Johnson ED, Beck KL, Pardini RS. Key roles forGRB2-associated-binding protein1, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase, cyclooxygenase 2, prostaglandin E2 and transforming growth factor alpha in linoleic acid-inducedupregulation of lung and breast cancer cell growth. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2014;90:105–115. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2013.12.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa040938. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
