From ArrayExpress to BioStudies
- PMID: 33211879
- PMCID: PMC7778911
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1062
From ArrayExpress to BioStudies
Abstract
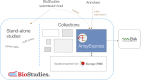
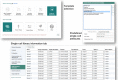
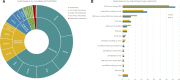
ArrayExpress (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress) is an archive of functional genomics data at EMBL-EBI, established in 2002, initially as an archive for publication-related microarray data and was later extended to accept sequencing-based data. Over the last decade an increasing share of biological experiments involve multiple technologies assaying different biological modalities, such as epigenetics, and RNA and protein expression, and thus the BioStudies database (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/biostudies) was established to deal with such multimodal data. Its central concept is a study, which typically is associated with a publication. BioStudies stores metadata describing the study, provides links to the relevant databases, such as European Nucleotide Archive (ENA), as well as hosts the types of data for which specialized databases do not exist. With BioStudies now fully functional, we are able to further harmonize the archival data infrastructure at EMBL-EBI, and ArrayExpress is being migrated to BioStudies. In future, all functional genomics data will be archived at BioStudies. The process will be seamless for the users, who will continue to submit data using the online tool Annotare and will be able to query and download data largely in the same manner as before. Nevertheless, some technical aspects, particularly programmatic access, will change. This update guides the users through these changes.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ArrayExpress update - from bulk to single-cell expression data.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jan 8;47(D1):D711-D715. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky964. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30357387 Free PMC article.
-
ArrayExpress update--simplifying data submissions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jan;43(Database issue):D1113-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1057. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25361974 Free PMC article.
-
ArrayExpress update--an archive of microarray and high-throughput sequencing-based functional genomics experiments.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan;39(Database issue):D1002-4. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1040. Epub 2010 Nov 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21071405 Free PMC article.
-
Data storage and analysis in ArrayExpress.Methods Enzymol. 2006;411:370-86. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(06)11020-4. Methods Enzymol. 2006. PMID: 16939801 Review.
-
Reuse of public genome-wide gene expression data.Nat Rev Genet. 2013 Feb;14(2):89-99. doi: 10.1038/nrg3394. Epub 2012 Dec 27. Nat Rev Genet. 2013. PMID: 23269463 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Expression Enrichment Tool (DEET): an interactive atlas of human differential gene expression.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2023 Jan 23;5(1):lqad003. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqad003. eCollection 2023 Mar. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 36694664 Free PMC article.
-
GeTeSEPdb: A comprehensive database and online tool for the identification and analysis of gene profiles with temporal-specific expression patterns.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024 Jun 5;23:2488-2496. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.06.003. eCollection 2024 Dec. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 38939556 Free PMC article.
-
CTR-DB, an omnibus for patient-derived gene expression signatures correlated with cancer drug response.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jan 7;50(D1):D1184-D1199. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab860. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 34570230 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence and machine-learning approaches in structure and ligand-based discovery of drugs affecting central nervous system.Mol Divers. 2023 Apr;27(2):959-985. doi: 10.1007/s11030-022-10489-3. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Mol Divers. 2023. PMID: 35819579 Review.
-
ARGEOS: A New Bioinformatic Tool for Detailed Systematics Search in GEO and ArrayExpress.Biology (Basel). 2021 Oct 11;10(10):1026. doi: 10.3390/biology10101026. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34681124 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brazma A., Hingamp P., Quackenbush J., Sherlock G., Spellman P., Stoeckert C., Aach J., Ansorge W., Ball C.A., Causton H.C.. Minimum information about a microarray experiment (MIAME)—toward standards for microarray data. Nat. Genet. 2001; 29:365–371. - PubMed
-
- Parkinson H., Sarkans U., Kolesnikov N., Abeygunawardena N., Burdett T., Dylag M., Emam I., Farne A., Hastings E., Holloway E. et al. .. ArrayExpress update–an archive of microarray and high-throughput sequencing-based functional genomics experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011; 39:D1002–D1004. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

