CircTBL1XR1/miR-424 axis regulates Smad7 to promote the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer
- PMID: 33209488
- PMCID: PMC7657834
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-20-395
CircTBL1XR1/miR-424 axis regulates Smad7 to promote the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: This study analyzed the effect of circular RNA (circRNA), TBL1XR1, on the malignant progression of colon cancer cells and explored its possible molecular mechanism.
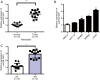
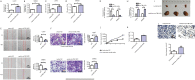
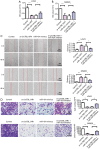
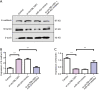
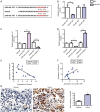
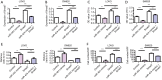
Methods: The expression levels of circTBL1XR1 in colorectal cancer and paracancerous tissues were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain (qRT-PCR). Changes in circTBL1XR1 expression in normal intestinal epithelial cells and colon cancer cell lines were detected at the cellular level. LoVo and SW620 cells with the highest circTBL1XR1 expression were transfected with circTBL1XR1, and the transfection efficiency was verified by qRT-PCR. The effects of circTBL1XR1 on the proliferation, migration, and invasion of colon cancer cells were detected by MTT, Transwell migration, and invasion assay, and a subcutaneous tumor model. Target genes of circTBL1XR1 were verified by luciferase reporter assay. Expression levels of circTBL1XR1 target genes were detected by qRT-PCR and Western blotting.
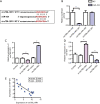
Results: circTBL1XR1 was highly expressed in colon cancer patients. circTBL1XR1 expression in colon cancer cells was also higher than that in normal intestinal cells. In vivo and in vitro experimental results showed that overexpression of circTBL1XR1 enhanced the proliferation, migration, and invasion of colon cancer cells. After lowering circTBL1XR1, the ability of migration and invasion of colon cancer cells was significantly reduced. Bioinformatics retrieval and luciferase reporter gene assay confirmed that circTBL1XR1 can bind to microRNA-424 (miR-424) and that the Smad7 gene is the target gene of miR-424.
Conclusions: circTBL1XR1 was highly expressed in colon cancer, and miR-424 was poorly expressed in colon cancer cells. circTBL1XR1 regulates the expression of Smad7 through miR-424, thereby affecting the malignant progression of colorectal cancer.
Keywords: Smad7; circTBL1XR1; colorectal cancer; epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT); miR-424.
2020 Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The author has completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/jgo-20-395). The author has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CircPRKCI regulates proliferation, migration and cycle of lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting miR-219a-5p-regulated CAMK1D.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Feb;25(4):1899-1909. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202102_25085. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33660800
-
miR-887-3p Inhibits the Progression of Colorectal Cancer via Downregulating DNMT1 Expression and Regulating P53 Expression.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Jun 27;2022:7179733. doi: 10.1155/2022/7179733. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9831724. doi: 10.1155/2023/9831724 PMID: 35795731 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The CircRNA-ACAP2/Hsa-miR-21-5p/ Tiam1 Regulatory Feedback Circuit Affects the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Colon Cancer SW480 Cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(4):1539-1550. doi: 10.1159/000493457. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30212824
-
Hsa_circRNA_001859 regulates pancreatic cancer progression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the miR-21-5p/SLC38A2 pathway.Cancer Biomark. 2023;37(1):39-52. doi: 10.3233/CBM-220229. Cancer Biomark. 2023. PMID: 37005877 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-424-5p participates in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma invasion and metastasis via SMAD7 pathway mediated EMT.Diagn Pathol. 2016 Sep 15;11(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13000-016-0536-9. Diagn Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27628042 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Correlation between SMADs and Colorectal Cancer Expression, Prognosis, and Immune Infiltrates.Int J Anal Chem. 2023 Mar 8;2023:8414040. doi: 10.1155/2023/8414040. eCollection 2023. Int J Anal Chem. 2023. PMID: 36969909 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Smad7 in Inflammatory Diseases of the Gut and Colon Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 10;22(8):3922. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083922. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33920230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The hsa_circ_0039857/miR-338-3p/RAB32 axis promotes the malignant progression of colorectal cancer.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Dec 20;22(1):530. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02622-1. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36539702 Free PMC article.
-
The Dual Role of Circular RNAs as miRNA Sponges in Breast Cancer and Colon Cancer.Biomedicines. 2021 Oct 31;9(11):1590. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111590. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of miR-424 in the carcinogenesis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 Jan;26(1):16-38. doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03209-2. Epub 2023 May 13. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 37178445 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
