High-density lipoprotein cholesterol is a predictor of survival in cirrhotic patients with acute gastrointestinal bleeding: a retrospective study
- PMID: 33198637
- PMCID: PMC7667781
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-020-01522-6
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol is a predictor of survival in cirrhotic patients with acute gastrointestinal bleeding: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Lipid profiles are declined in patients with viral liver cirrhosis and correlated with severity of liver disease. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is the leading cause of liver cirrhosis in China. Our primary aim was to investigate whether serum lipids and lipoproteins associate with survival in patients with HBV-related cirrhosis and acute gastrointestinal bleeding, and develop a 6-week mortality risk score that incorporates it.
Methods: From January 2008 to December 2015, consecutive cirrhotic patients with acute gastrointestinal bleeding admitted to our hospital were evaluated and randomly divided into the derivation (n = 629) and validation (n = 314) cohorts. A logistic regression model was established to confirm the association between lipoprotein cholesterol and mortality. Accuracy to predict mortality were assessed by area under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUROCs) and compared using the Hanley and McNeil test.
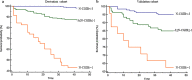
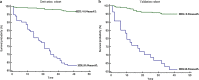
Results: Among study subjects, the 6-week mortality rate was 10.6%. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) level was found to correlate most strongly with prognostic scores. On ROC analysis, HDL-C showed excellent diagnostic accuracy for 6-week mortality. Logistic regression analysis provided a simple algorithm based on the combined use of 4 variables (total bilirubin (TBIL), HDL-C, International normalized ratio, and hemoglobin), allowing accurate discrimination of 3 distinct prognostic subgroups with 1.7% (low risk), 12.3% (intermediate risk), and 56.9% (high risk) mortality. Its accuracy was significantly better than that of Child-Pugh, model of end-stage liver disease, albumin-bilirubin score, D'Amico model, Augustin model, AIMS65 score and Glasgow-Blatchford score. Baseline HDL-C values ≤ 0.54 mmol/L were associated with markedly lower 6-week survival. Comparable results were found in the validation set.
Conclusion: HDL-C is a potential indicator for the prognosis of patients with cirrhosis and acute gastrointestinal bleeding. The new algorithm based on HDL-C allowed an accurate predictive assessment of 6-week mortality after bleeding attack.
Keywords: 6-Week mortality; Acute gastrointestinal bleeding; High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; Liver cirrhosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development and Validation of a Scoring System That Includes Corrected QT Interval for Risk Analysis of Patients With Cirrhosis and Gastrointestinal Bleeding.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Jun;17(7):1388-1397.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.12.006. Epub 2018 Dec 15. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30557740
-
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol for the prediction of mortality in cirrhosis with portal vein thrombosis: a retrospective study.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Mar 30;18(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1005-8. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 30927926 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of risk scoring systems for cirrhotic patients with variceal bleeding.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Dec 7;25(45):6668-6680. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i45.6668. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31832005 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of CAGIB Score for Evaluating the Prognosis of Cirrhosis with Acute Gastrointestinal Bleeding: A Retrospective Multicenter Study.Adv Ther. 2019 Nov;36(11):3211-3220. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-01083-5. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Adv Ther. 2019. PMID: 31512140 Free PMC article.
-
QTc interval prolongation in liver cirrhosis with upper gastrointestinal bleeding.Med Clin (Barc). 2021 Jan 22;156(2):68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2020.06.059. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Med Clin (Barc). 2021. PMID: 33309043 Review. English, Spanish.
Cited by
-
Metabolomic serum abnormalities in dogs with hepatopathies.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 29;12(1):5329. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09056-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35351920 Free PMC article.
-
Role of High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C) as a Clinical Predictor of Decompensation in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease (CLD).Int J Hepatol. 2021 Dec 24;2021:1795851. doi: 10.1155/2021/1795851. eCollection 2021. Int J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34976412 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Low High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels with Poor Outcomes in Hepatitis B-Associated Decompensated Cirrhosis Patients.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Jul 27;2021:9927330. doi: 10.1155/2021/9927330. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34355041 Free PMC article.
-
Role of triglycerides as a predictor of autoimmune hepatitis with cirrhosis.Lipids Health Dis. 2022 Oct 25;21(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s12944-022-01716-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2022. PMID: 36284329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- A A, G I-S, J P, et al. Survival of patients with cirrhosis and acute peptic ulcer bleeding compared with variceal bleeding using current first-line therapies. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md). 2018;67(4):1458–1471. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. 2017ZX10302201/The National Science and Technology Major Project for Infectious Diseases
- No. 2017ZX10203202/The National Science and Technology Major Project for Infectious Diseases
- No. 2018ZX09201016/The National Science and Technology Major Special Project for New Drug Development
- No. D161100002716002/Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission of Major Projects
- No. D161100002716003/Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission of Major Projects
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

