Factors and Molecular Mechanisms Influencing the Protein Synthesis, Degradation and Membrane Trafficking of ASIC1a
- PMID: 33195276
- PMCID: PMC7644914
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.596304
Factors and Molecular Mechanisms Influencing the Protein Synthesis, Degradation and Membrane Trafficking of ASIC1a
Abstract
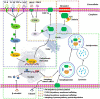
Acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) are members of the degenerin/epithelial sodium channel superfamily. They are extracellular pH sensors that are activated by protons. Among all ASICs, ASIC1a is one of the most intensively studied isoforms because of its unique ability to be permeable to Ca2+. In addition, it is considered to contribute to various pathophysiological conditions. As a membrane proton receptor, the number of ASIC1a present on the cell surface determines its physiological and pathological functions, and this number partially depends on protein synthesis, degradation, and membrane trafficking processes. Recently, several studies have shown that various factors affect these processes. Therefore, this review elucidated the major factors and underlying molecular mechanisms affecting ASIC1a protein expression and membrane trafficking.
Keywords: acid-sensing ion channel 1a; factors; membrane trafficking; molecular mechanisms; protein expression.
Copyright © 2020 Xu and Chen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Permeating protons contribute to tachyphylaxis of the acid-sensing ion channel (ASIC) 1a.J Physiol. 2007 Mar 15;579(Pt 3):657-70. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.120733. Epub 2007 Jan 4. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17204502 Free PMC article.
-
Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a Is Involved in N-Methyl D-Aspartate Receptor-Dependent Long-Term Depression in the Hippocampus.Front Pharmacol. 2019 May 21;10:555. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00555. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31178731 Free PMC article.
-
Acid-sensing ion channel 1a is required for mGlu receptor dependent long-term depression in the hippocampus.Pharmacol Res. 2017 May;119:12-19. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.01.028. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 28137639
-
Peptides inhibitors of acid-sensing ion channels.Toxicon. 2007 Feb;49(2):271-84. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2006.09.026. Epub 2006 Oct 4. Toxicon. 2007. PMID: 17113616 Review.
-
Acid-sensing ion channels: trafficking and pathophysiology.Channels (Austin). 2014;8(6):481-7. doi: 10.4161/19336950.2014.958382. Channels (Austin). 2014. PMID: 25483283 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acid-sensing ion channel 1 contributes to pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell depolarization following hypoxic pulmonary hypertension.J Physiol. 2021 Nov;599(21):4749-4762. doi: 10.1113/JP282231. Epub 2021 Sep 25. J Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34487355 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of ASIC1a in Inflammatory Immune Diseases: A Potential Therapeutic Target.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 8;13:942209. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.942209. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35873582 Free PMC article.
-
Nesfatin-1 exerts protective effects on acidosis-stimulated chondrocytes and rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis by inhibiting ASIC1a expression.Lab Invest. 2022 Aug;102(8):859-871. doi: 10.1038/s41374-022-00774-y. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Lab Invest. 2022. PMID: 35292759
-
Acid-Sensing Ion Channel-1a in Articular Chondrocytes and Synovial Fibroblasts: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 28;11:580936. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.580936. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33584647 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

