Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Induced Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
- PMID: 33194467
- PMCID: PMC7657311
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.10898
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Induced Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
Abstract
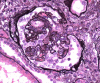
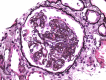
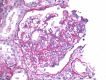
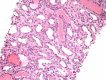
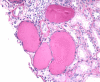
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a common cause of nephrotic syndrome affecting adults and children. Collapsing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), one of five histologic variants of FSGS is described as segmental or global collapse and sclerosis of the glomerular tufts and has been frequently associated with human immunodeficiency virus-associated nephropathy (HIVAN). Its association with other viral and non-viral causes, medications and other disease states has since been established. Due to its resistance to therapy, rapid progression to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and overall poorer prognosis, identification with electron microscopy examination of the kidney biopsy sample is required during evaluation.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; apol1 gene; collapsing fsgs; covid-19; esrd; focal segmental glomerulosclerosis; fsgs; proteinuria; sars-cov-2; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Copyright © 2020, Malik et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIV-associated nephropathy: experimental models.Contrib Nephrol. 2011;169:270-285. doi: 10.1159/000320212. Epub 2011 Jan 20. Contrib Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21252526
-
Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis: does prognosis vary with the variants?Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2015 Jan;26(1):173-81. doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.148772. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2015. PMID: 25579744
-
COVID-19-Related Glomerulopathy: A Report of 2 Cases of Collapsing Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis.Kidney Med. 2020 Jun 7;2(4):488-492. doi: 10.1016/j.xkme.2020.05.004. eCollection 2020 Jul-Aug. Kidney Med. 2020. PMID: 32775989 Free PMC article.
-
Collapsing Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis in Viral Infections.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 13;12:800074. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.800074. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35095882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis after renal transplantation.Clin Transplant. 2011 Jul;25 Suppl 23:6-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2011.01452.x. Clin Transplant. 2011. PMID: 21623907 Review.
Cited by
-
FSGS and COVID-19 in Non-African American Patients.Kidney360. 2023 May 1;4(5):687-699. doi: 10.34067/KID.0000000000000104. Kidney360. 2023. PMID: 37229730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Collapsing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis secondary to COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Feb 7;85(2):92-101. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000000107. eCollection 2023 Feb. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023. PMID: 36845824 Free PMC article.
-
Native and transplant kidney histopathological manifestations in association with COVID-19 infection: A systematic review.World J Transplant. 2021 Nov 18;11(11):480-502. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v11.i11.480. World J Transplant. 2021. PMID: 34868898 Free PMC article.
-
Acute and chronic histopathological findings in renal biopsies in COVID-19.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Aug;23(4):1003-1014. doi: 10.1007/s10238-022-00941-x. Epub 2022 Nov 18. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36396750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Case of COVID-19-Associated Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis.Cureus. 2023 Apr 13;15(4):e37547. doi: 10.7759/cureus.37547. eCollection 2023 Apr. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37193424 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
