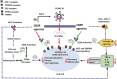
CB2 receptor-selective agonists as candidates for targeting infection, inflammation, and immunity in SARS-CoV-2 infections
- PMID: 33190277
- PMCID: PMC7753678
- DOI: 10.1002/ddr.21752
CB2 receptor-selective agonists as candidates for targeting infection, inflammation, and immunity in SARS-CoV-2 infections
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 is a deadly disease afflicting millions. The pandemic continues affecting population due to nonavailability of drugs and vaccines. The pathogenesis and complications of infection mainly involve hyperimmune-inflammatory responses. Thus, therapeutic strategies rely on repurposing of drugs aimed at reducing infectivity and inflammation and modulate immunity favourably. Among, numerous therapeutic targets, the endocannabinoid system, particularly activation of cannabinoid type-2 receptors (CB2R) emerged as an important one to suppress the hyperimmune-inflammatory responses. Recently, potent antiinflammatory, antiviral and immunomodulatory properties of CB2R selective ligands of endogenous, plant, and synthetic origin were showed mediating CB2R selective functional agonism. CB2R activation appears to regulate numerous signaling pathways to control immune-inflammatory mediators including cytokines, chemokines, adhesion molecules, prostanoids, and eicosanoids. Many CB2R ligands also exhibit off-target effects mediating activation of PPARs, opioids, and TRPV, suggestive of adjuvant use with existing drugs that may maximize efficacy synergistically and minimize therapeutic doses to limit adverse/ side effects. We hypothesize that CB2R agonists, due to immunomodulatory, antiinflammatory, and antiviral properties may show activity against COVID-19. Based on the organoprotective potential, relative safety, lack of psychotropic effects, and druggable properties, CB2R selective ligands might make available promising candidates for further investigation.
Keywords: COVID-19; cannabinoids; immunomodulators; inflammation.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
β-Caryophyllene, A Natural Dietary CB2 Receptor Selective Cannabinoid can be a Candidate to Target the Trinity of Infection, Immunity, and Inflammation in COVID-19.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 14;12:590201. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.590201. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34054510 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Cannabinoid 2 Receptor Agonists as Potential Therapeutic Drugs for the Treatment of Endotoxin-Induced Uveitis.Molecules. 2019 Sep 13;24(18):3338. doi: 10.3390/molecules24183338. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31540271 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Agonists from Botanical Compounds and Preliminary Evaluation of Their Anti-Osteoporotic Effects.Molecules. 2022 Jan 21;27(3):702. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030702. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35163968 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological potential of JWH133, a cannabinoid type 2 receptor agonist in neurodegenerative, neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric diseases.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 15;909:174398. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174398. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34332924 Review.
-
A focused review on CB2 receptor-selective pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential of β-caryophyllene, a dietary cannabinoid.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Aug;140:111639. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111639. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34091179 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Vesicle-Based Therapy for COVID-19: Promises, Challenges and Future Prospects.Biomedicines. 2021 Oct 1;9(10):1373. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101373. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34680490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-based virtual screening methods for the identification of novel phytochemical inhibitors targeting furin protease for the management of COVID-19.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jun 11;14:1391288. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1391288. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38919703 Free PMC article.
-
The results of a unique dietary supplement (nutraceutical formulation) used to treat the symptoms of long-haul COVID.Front Nutr. 2022 Oct 25;9:1034169. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1034169. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36386945 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Antioxidants for the Neuro-Therapeutic Management of COVID-19.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jun 17;10(6):971. doi: 10.3390/antiox10060971. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34204362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating endocannabinoid levels in SARS-CoV-2 infection and their potential role in the inflammatory response.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 22;14(1):19558. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70172-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39174572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Channappanavar, R. , Fehr, A. R. , Vijay, R. , Mack, M. , Zhao, J. , Meyerholz, D. K. , & Perlman, S. (2016). Dysregulated type I interferon and inflammatory monocyte‐macrophage responses cause lethal pneumonia in SARS‐CoV‐infected mice. Cell Host & Microbe, 19(2), 181–193. 10.1016/j.chom.2016.01.007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous