Mechanical Allodynia Circuitry in the Dorsal Horn Is Defined by the Nature of the Injury
- PMID: 33181066
- PMCID: PMC7806207
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.10.027
Mechanical Allodynia Circuitry in the Dorsal Horn Is Defined by the Nature of the Injury
Abstract
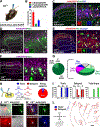
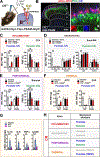
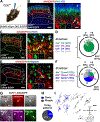
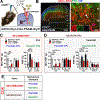
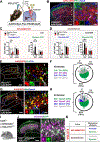
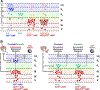
The spinal dorsal horn is a major site for the induction and maintenance of mechanical allodynia, but the circuitry that underlies this clinically important form of pain remains unclear. The studies presented here provide strong evidence that the neural circuits conveying mechanical allodynia in the dorsal horn differ by the nature of the injury. Calretinin (CR) neurons in lamina II inner convey mechanical allodynia induced by inflammatory injuries, while protein kinase C gamma (PKCγ) neurons at the lamina II/III border convey mechanical allodynia induced by neuropathic injuries. Cholecystokinin (CCK) neurons located deeper within the dorsal horn (laminae III-IV) are important for both types of injuries. Interestingly, the Maf+ subset of CCK neurons is composed of transient vesicular glutamate transporter 3 (tVGLUT3) neurons, which convey primarily dynamic allodynia. Identification of an etiology-based circuitry for mechanical allodynia in the dorsal horn has important implications for the mechanistic and clinical understanding of this condition.
Keywords: calretinin; cholecystokinin; dorsal horn; inflammatory pain; mechanical allodynia; neural circuitry; neuropathic pain; pain; protein kinase C gamma; vesicular glutamate transporter 3.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Sensory Symphonies: How Excitatory Spinal Cord Modules Orchestrate Behavior.Neuron. 2021 Jan 6;109(1):3-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.12.012. Neuron. 2021. PMID: 33412095 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Dorsal Horn Circuits for Persistent Mechanical Pain.Neuron. 2015 Aug 19;87(4):797-812. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.07.029. Neuron. 2015. PMID: 26291162 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation is downstream coupled to pannexin 1 opening by Src kinase in dorsal horn neurons: an essential link for mechanical hyperalgesia in nerve-injured rats.Pain. 2024 Dec 3. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003476. Online ahead of print. Pain. 2024. PMID: 39630026
-
PACAP/PAC1-R activation contributes to hyperalgesia in 6-OHDA-induced Parkinson's disease model rats via promoting excitatory synaptic transmission of spinal dorsal horn neurons.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023 Dec;44(12):2418-2431. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01141-3. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023. PMID: 37563446 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuron-specific spinal cord translatomes reveal a neuropeptide code for mouse dorsal horn excitatory neurons.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 4;11(1):5232. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84667-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33664406 Free PMC article.
-
Organic anion transporter 1 is an HDAC4-regulated mediator of nociceptive hypersensitivity in mice.Nat Commun. 2022 Feb 15;13(1):875. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28357-x. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35169129 Free PMC article.
-
Z-Guggulsterone Relieves Neuropathic Pain by Inhibiting the Expression of Astrocytes and Proinflammatory Cytokines in the Spinal Dorsal Horn.J Pain Res. 2022 May 5;15:1315-1324. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S360126. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 35546904 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Pain-Related Jaw Muscle Motor Load and Sensory Processing.J Dent Res. 2022 Sep;101(10):1165-1171. doi: 10.1177/00220345221099885. Epub 2022 Jun 16. J Dent Res. 2022. PMID: 35708459 Free PMC article.
-
Modality-Specific Modulation of Temperature Representations in the Spinal Cord after Injury.J Neurosci. 2021 Sep 29;41(39):8210-8219. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1104-21.2021. Epub 2021 Aug 18. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34408066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alba-Delgado C, El Khoueiry C, Peirs C, Dallel R, Artola A, and Antri M (2015). Subpopulations of PKCgamma interneurons within the medullary dorsal horn revealed by electrophysiologic and morphologic approach. Pain 156, 1714–1728. - PubMed
-
- Artola A, Voisin D, and Dallel R (2020). PKCgamma interneurons, a gateway to pathological pain in the dorsal horn. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 127, 527–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

