Analysis of METTL3 and METTL14 in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 33159022
- PMCID: PMC7695415
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.103959
Analysis of METTL3 and METTL14 in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
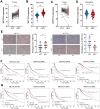
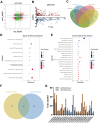
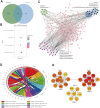
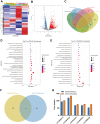
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA methylation is the most prevalent modification of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) and catalyzed by a multicomponent methyltransferase complex (MTC), among which methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) and METTL14 are two core molecules. However, METTL3 and METTL14 play opposite regulatory roles in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Based on The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, we conducted a multi-omics analysis of METTL3 and METTL14 in HCC, including RNA-sequencing, m6ARIP-sequencing, and ribosome-sequencing profiles. We found that the expression and prognostic value of METTL3 and METTL14 are opposite in HCC. Besides, after METTL3 and METTL14 knockdown, most of the dysregulated mRNAs, signaling pathways and biological processes are distinct in HCC, which partly explains the contrary regulatory role of METTL3 and METTL14. Intriguingly, these mRNAs whose stability or translation efficiency are influenced by METTL3 or METTL14 in an m6A dependent manner, jointly regulate multiple signaling pathways and biological processes, which supports the cooperative role of METTL3 and METTL14 in catalyzing m6A modification. In conclusion, our study further clarified the contradictory role of METTL3 and METTL14 in HCC.
Keywords: METTL14; METTL3; N6-methyladenosine; bioinformatics analysis; hepatocellular carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
METTL3 regulates m6A in endometrioid epithelial ovarian cancer independently of METTl14 and WTAP.Cell Biol Int. 2020 Dec;44(12):2524-2531. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11459. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Cell Biol Int. 2020. PMID: 32869897
-
HBXIP drives metabolic reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via METTL3-mediated m6A modification of HIF-1α.J Cell Physiol. 2021 May;236(5):3863-3880. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30128. Epub 2020 Dec 11. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33305825
-
Identification of three m6A-related mRNAs signature and risk score for the prognostication of hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2020 Mar;9(5):1877-1889. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2833. Epub 2020 Jan 13. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 31943856 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into roles of METTL14 in tumors.Cell Prolif. 2022 Jan;55(1):e13168. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13168. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Cell Prolif. 2022. PMID: 34904301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in post-transcriptional gene expression regulation.Genes Dev. 2015 Jul 1;29(13):1343-55. doi: 10.1101/gad.262766.115. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 26159994 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
m6A Regulator-Associated Modification Patterns and Immune Infiltration of the Tumor Microenvironment in Hepatocarcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul 2;9:687756. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.687756. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34277630 Free PMC article.
-
The role of RNA modifications in hepatocellular carcinoma: functional mechanism and potential applications.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 20;15:1439485. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1439485. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39229278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
METTL protein family: focusing on the occurrence, progression and treatment of cancer.Biomark Res. 2024 Sep 17;12(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00652-3. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39289775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic m6A-ncRNAs association and their impact on cancer pathogenesis, immune regulation and therapeutic response.Genes Dis. 2021 Nov 10;10(1):135-150. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2021.10.004. eCollection 2023 Jan. Genes Dis. 2021. PMID: 37013031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA m6A modification in liver biology and its implication in hepatic diseases and carcinogenesis.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 Oct 1;323(4):C1190-C1205. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00214.2022. Epub 2022 Aug 29. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36036444 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

